Solar Radiation and Earth's Seasons
Grace Taylor
6 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers solar radiation, its dependence on latitude and how it influences seasons. It explains the Earth's tilt (23.5°) and its effect on day length, temperature, and the occurrence of equinoxes and solstices. It also provides tips and practice questions for the AP Environmental Science exam related to these concepts.
#AP Environmental Science: Solar Radiation, Seasons, and Earth's Tilt Study Guide
Hey there, future AP Environmental Science master! Let's break down solar radiation, seasons, and Earth's tilt. This is crucial stuff, and we'll make sure it sticks. Let's get started!
#☀️ Solar Radiation and Latitude
#The Sun: Our Main Energy Source
- The sun is the primary source of energy for Earth, and this energy is called solar radiation. 💡
- Solar radiation affects biomes differently based on the season and latitude.
#Seasonal Changes
- Daylight Hours: The length of day and night changes with the seasons.
- Winter: Shorter days, longer nights, less direct solar radiation.
- Summer: Longer days, shorter nights, more direct solar radiation.
#Latitude's Impact
- Equator (0° Latitude): Solar radiation hits directly, resulting in more energy per unit area. 🔥
- Higher Latitudes: Due to Earth's curvature, solar radiation is spread over a larger area, leading to less energy per unit area.
The angle at which sunlight hits the Earth's surface is a critical factor in determining the amount of solar energy received. Direct sunlight (at the equator) is more intense than angled sunlight (at higher latitudes).
#🌍 Seasons and Earth's Tilt
#Earth's Tilt and Seasons
- Earth's tilt on its axis (about 23.5°) is the reason we have seasons. 🔄
- As Earth orbits the sun, different parts of the planet receive more or less direct sunlight.
#How Tilt Affects Temperature
- Tilt Towards the Sun:
- Longer days, more direct sunlight, warmer temperatures.
- Tilt Away from the Sun:
- Longer nights, less direct sunlight, colder temperatures.
#Equinoxes vs. Solstices
- Equinoxes:
- Occur in spring and fall/autumn.
- Day and night are approximately equal in length. ⚖️
- Earth's tilt is neither towards nor away from the sun.
- Solstices:
- Summer and winter solstices.
- Represent the longest and shortest days of the year. ☀️/🌑
- Earth's tilt is most directly towards or away from the sun.
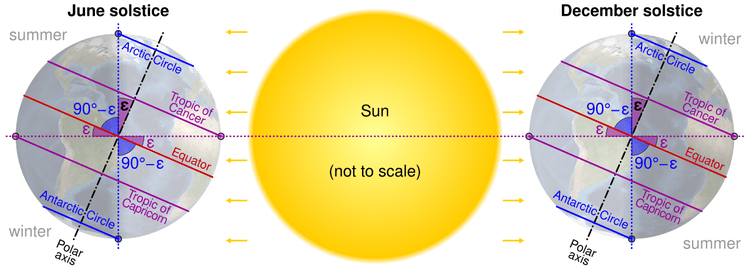
#Image Courtesy of Wikimedia
Equinox = Equal Day and Night. Think of 'equi' meaning equal. Solstice = Sun's Standstill. Think of the sun reaching its highest or lowest point.
Don't mix up equinoxes and solstices! Equinoxes are about equal day and night, while solstices are about the extremes of daylight.
#Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics
- Relationship between solar radiation, latitude, and seasons.
- Understanding Earth's tilt and its impact on day length and temperature.
- Distinguishing between equinoxes and solstices.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Expect questions on how solar radiation varies with latitude and season, and the effects of Earth's tilt.
- Free Response: Be prepared to explain the mechanisms behind seasons and how they impact different regions.
#Last-Minute Tips
-
Time Management: Quickly identify the core concept in each question.
-
Common Pitfalls: Avoid confusing equinoxes and solstices. Double-check your understanding of how Earth's tilt affects solar radiation.
-
Strategies: Use diagrams to visualize the Earth's tilt and sunlight angles. Practice explaining the concepts out loud.
This topic is foundational to many other concepts in environmental science. Understanding solar radiation and seasons is crucial for understanding climate, biomes, and energy flow.
Earth's tilt is 23.5 degrees. This is a key number to remember!
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the relationship between latitude and solar radiation? a) Solar radiation is evenly distributed across all latitudes. b) Higher latitudes receive more direct solar radiation than lower latitudes. c) The equator receives more direct solar radiation than higher latitudes. d) Solar radiation is not affected by latitude.
-
What is the primary cause of the seasons on Earth? a) Changes in the Earth's distance from the sun. b) The Earth's rotation on its axis. c) The Earth's tilt on its axis. d) The amount of solar radiation emitted by the sun.
-
During which of the following times of the year is the Earth's axis tilted neither toward nor away from the Sun? a) Summer solstice b) Winter solstice c) Equinoxes d) All of the above
#Free Response Question
Explain how the Earth's tilt on its axis and its orbit around the sun result in the seasons. In your explanation, be sure to:
a) Describe the position of the Earth relative to the sun during the summer and winter solstices.
b) Describe the position of the Earth relative to the sun during the spring and fall equinoxes.
c) Explain how the angle of solar radiation affects the intensity of sunlight received at different latitudes.
d) Discuss how the length of day and night varies with the seasons and latitude.
Scoring Rubric
- (a) Summer and Winter Solstices (2 points):
- 1 point for correctly stating that during the summer solstice, the Earth's axis is tilted toward the sun in the Northern Hemisphere (and vice versa for Southern Hemisphere).
- 1 point for correctly stating that during the winter solstice, the Earth's axis is tilted away from the sun in the Northern Hemisphere (and vice versa for Southern Hemisphere).
- (b) Spring and Fall Equinoxes (2 points):
- 1 point for correctly stating that during the spring equinox, the Earth's axis is neither tilted toward nor away from the sun.
- 1 point for correctly stating that during the fall equinox, the Earth's axis is neither tilted toward nor away from the sun.
- (c) Angle of Solar Radiation (2 points):
- 1 point for stating that direct sunlight (at the equator) is more intense.
- 1 point for stating that angled sunlight (at higher latitudes) is less intense.
- (d) Length of Day and Night (2 points):
- 1 point for explaining that during summer, days are longer and nights are shorter, and vice versa for winter.
- 1 point for explaining that day length variation is more pronounced at higher latitudes and less at the equator.
Let's ace this exam! You got this!
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





