Increases in the Greenhouse Gases
Liam Thomas
8 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This AP Environmental Science study guide covers climate vs. weather, the greenhouse effect and key greenhouse gases (CO2, CH4, N2O, H2O, CFCs), the role of the IPCC, and the environmental impacts of climate change (rising sea levels, spread of disease, ocean acidification, extreme weather, and biodiversity loss). It also examines sources of greenhouse gases (natural and human) and provides practice questions and exam tips.
#AP Environmental Science: Climate Change Study Guide 🌍
Hey there! Let's get you prepped for the AP Environmental Science exam. This guide is designed to be your go-to resource, especially the night before the test. We'll break down the key concepts, make connections, and get you feeling confident. Let's do this!
#1. Understanding Climate vs. Weather
- Climate: Long-term (30+ years) weather patterns, including temperature and precipitation averages. Think of it as the 'usual' weather for a region. ☀️
- Weather: Short-term atmospheric conditions. Think of it as what's happening outside right now. 🌧️
Climate change is about shifts in long-term averages, not just day-to-day weather.
#2. The Greenhouse Effect & Gases
- Greenhouse Effect: A natural process where gases in the troposphere trap thermal energy, keeping Earth warm enough to support life. 🌡️
- Greenhouse Gases (GHGs): Gases that trap heat. Increased concentrations lead to more trapped heat and higher average global temperatures.
#Key Greenhouse Gases:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Major contributor from fossil fuel combustion. 🔥
- Also from deforestation and industrial processes.
- Methane (CH4):
- From agriculture (livestock), natural gas leaks, and landfills. 🐄
- More potent than CO2 over a shorter timeframe.
- Water Vapor (H2O):
- A feedback gas; increases with warming temperatures.
- Natural part of the water cycle.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O):
- From agricultural practices (fertilizers), industrial processes, and fossil fuel burning.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs):
- Synthetic compounds, formerly used in refrigerants and aerosols.
- Phased out due to ozone depletion, but still potent GHGs.
Remember "CO2, Methane, Water, N2O, CFCs" to quickly recall the main GHGs. Think of it as "Can My Wife Not Cook?"
#The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
- Formed in 1988, a group of 3,000+ scientists.
- Assesses climate change science, impacts, and risks.
- Provides crucial data and reports for policymakers. 📝
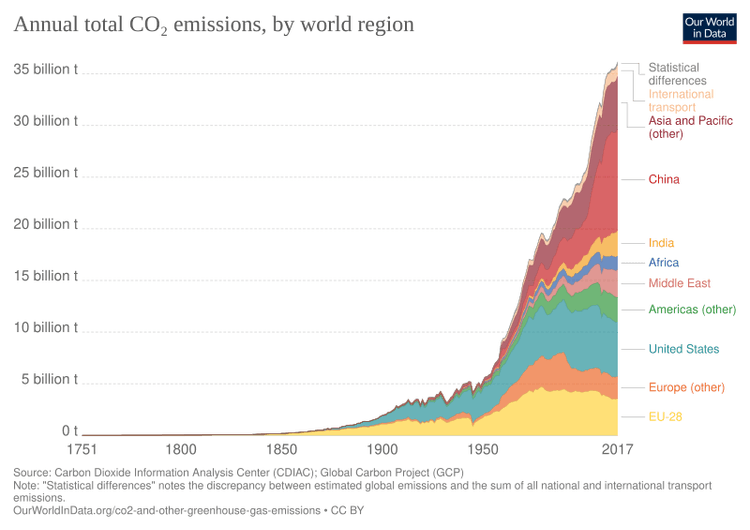
Be ready to discuss the IPCC's role and findings in FRQs. Focus on their data-driven approach and consensus on human-caused climate change.
Image Courtesy of Wikimedia
Caption: This graph illustrates the dramatic increase in CO2 emissions since the Industrial Revolution, highlighting the impact of human activities on atmospheric composition.
#3. Environmental Impacts of Climate Change
#Rising Sea Levels 🌊
- Melting of glaciers, ice caps, and ice sheets. 🧊
- Thermal expansion of water (warmer water takes up more space). 🌡️
- Leads to coastal flooding, erosion, and habitat loss.
#Spread of Disease Vectors 🦠🦟
- Warmer temperatures expand the range of disease vectors (e.g., mosquitoes, ticks). 🦟
- Increases the spread of diseases like malaria, dengue fever, and Lyme disease.
- Changes in host species distribution can also impact disease transmission.
#Ocean Acidification 🐚
- Increased CO2 in the atmosphere is absorbed by oceans. 🌊
- Forms carbonic acid, lowering ocean pH. 📉
- Impacts marine organisms with shells and skeletons (e.g., corals, shellfish). 🐚
#Extreme Weather Events & Changing Weather Patterns 🌧️
- Increased frequency and intensity of droughts, heatwaves, floods, and hurricanes. 🌪️
- Changes in atmospheric and oceanic circulation patterns.
- More evaporation leading to intense storms and rainfall.
#Loss of Biodiversity 🐘
- Species displacement due to habitat changes. 😥
- Extinction risk if species can't adapt or migrate. 🦧
- Disruptions to ecosystems and food chains.
- Increased competition for resources.
Don't confuse climate change with weather. Climate change is about long-term trends, not specific events. Also, remember that while climate change can increase the likelihood of extreme weather, it's hard to attribute any single event directly to it.
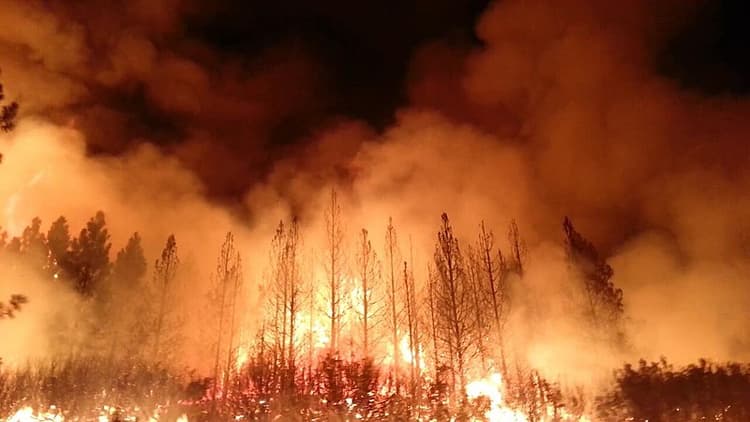

Image Courtesy of Wikimedia
Caption: Wildfires, like the Rim Fire shown here, are becoming more frequent and intense due to climate change, contributing to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.
#4. Sources of Greenhouse Gases
#Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Natural: Cellular respiration, volcanic eruptions, decomposition. 🌋
- Human: Fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, land-use changes, industrial processes. 🏭
#Methane (CH4)
- Natural: Wetlands, animal digestion, wildfires. 🔥
- Human: Fossil fuel extraction, landfills, agriculture (livestock), some industrial processes.
#Water Vapor (H2O)
- Natural: Evaporation, transpiration, respiration. 💧
- Human: Some industrial processes, agricultural activities.
#Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Natural: Soil decomposition, denitrification, lightning. ⚡
- Human: Agricultural activities (fertilizers), industrial production, fossil fuel burning.
#Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
- Human: Refrigerants, solvents, foam-blowing agents. 🧊
- (Note: largely phased out but still present in atmosphere)
The burning of fossil fuels is the largest contributor to increased CO2 emissions. Remember this for multiple-choice questions.
#5. Final Exam Focus
#High-Value Topics
- The Greenhouse Effect and Greenhouse Gases
- Impacts of Climate Change (Sea Level Rise, Ocean Acidification, Biodiversity Loss)
- Sources of Greenhouse Gases
- IPCC and Climate Change Science
Pay special attention to the interconnectedness of these topics. AP questions often combine multiple concepts (e.g., how deforestation impacts CO2 levels and biodiversity).
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Focus on definitions, sources of GHGs, and impacts of climate change. Expect data interpretation questions.
- Free Response Questions (FRQs): Expect to analyze graphs, propose solutions, and discuss environmental and economic impacts. Practice explaining cause-and-effect relationships.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. Move on and come back if needed. ⏰
- Read Carefully: Pay close attention to the question's wording. What is it really asking?
- Be Specific: Use scientific terms and be precise in your answers. Avoid vague statements.
- Show Your Work: For FRQs, clearly outline your reasoning and steps. Partial credit is your friend! 📝
- Stay Calm: You've got this! Take deep breaths and trust your preparation. 💪
For FRQs, always start by identifying the key components of the question. Then, use specific examples and data to support your claims. Practice outlining your answers before writing the full response.
#6. Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following is the MOST significant contributor to the increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide? (A) Volcanic eruptions (B) Deforestation (C) The burning of fossil fuels (D) The decay of organic matter
-
Which of the following is a consequence of increased ocean acidification? (A) Increased coral growth (B) Decreased ability of shellfish to form shells (C) Higher ocean pH levels (D) Increased fish populations
-
Which of the following is a greenhouse gas that is produced by the decomposition of organic matter in low-oxygen environments? (A) Carbon dioxide (B) Oxygen (C) Methane (D) Nitrogen
#Free Response Question
Scenario: A coastal community is experiencing increased flooding and erosion due to rising sea levels. The local government is considering various strategies to mitigate these impacts.
(a) Identify two specific human activities that contribute to rising sea levels. (2 points) (b) Describe one environmental consequence, other than flooding, that results from rising sea levels. (2 points) (c) Propose two different strategies that the community could implement to reduce the impacts of rising sea levels. For each strategy, explain how it would be effective. (4 points) (d) Explain one potential economic impact of implementing these strategies. (2 points)
Scoring Breakdown:
(a) (2 points total, 1 point per activity) - Acceptable answers include: Burning of fossil fuels, Deforestation, Industrial processes, etc.
(b) (2 points total, 1 point for identifying a consequence, 1 point for the description) - Acceptable answers include: Saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers, loss of coastal wetlands, increased erosion, loss of habitat for coastal species, etc.
(c) (4 points total, 2 points per strategy) - Acceptable answers include: Building sea walls or levees, restoring coastal wetlands, relocating vulnerable infrastructure, implementing stricter building codes, etc. Explanation of effectiveness must be included.
(d) (2 points total, 1 point for identifying an economic impact, 1 point for the explanation) - Acceptable answers include: Increased cost of infrastructure projects, decreased property values in vulnerable areas, increased insurance costs, job creation in green energy sectors, etc.
Good luck, you've got this! Let's ace that exam! 🚀
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





