Cost-Benefit Analysis
Paul Scott
8 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers cost-benefit analysis, including explicit and implicit costs and marginal analysis. It explains the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility and the Cost-Benefit Maximizing Principle (MB=MC). It also provides practice questions on these concepts and exam tips for the AP Microeconomics exam.
#AP Microeconomics: Cost-Benefit Analysis - Your Last-Minute Guide
Hey there! Let's make sure you're totally ready for the AP Microeconomics exam. We'll go through cost-benefit analysis, marginal analysis, and everything in between. Let's get started!
#1. Introduction to Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is the core of making smart economic decisions. It's all about weighing the costs against the benefits of a choice. Think of it as your superpower for deciding if something is worth it.
#What is it?
- A method to evaluate if a project or policy's benefits outweigh its costs.
- Used in business, government, and non-profits to make informed decisions.
- Helps in resource allocation and investment strategies.
#2. Diving into Costs: Explicit vs. Implicit
#Explicit Costs
- Definition: Direct, out-of-pocket monetary costs. Think of these as the obvious costs.
- Examples: Raw materials, wages, rent, utilities, insurance. These are all things you write a check for.
- Accounting: Recorded in a company's financial statements.
#Implicit Costs
- Definition: Indirect costs, also known as opportunity costs. They are the value of the next best alternative you give up.
- Examples: The salary you could have earned if you weren't in school, the return you could have earned if you invested your money elsewhere.
- Key Idea: Not recorded in accounting, but crucial for economic decision-making.
Explicit costs are like expenses you can see and touch, while implicit costs are the implied value of what you're missing out on.
#3. Marginal Analysis: Benefit and Cost
#Total vs. Marginal
- Total Benefit/Cost: The overall benefit or cost from consuming a certain quantity of goods or services.
- Marginal Benefit/Cost: The additional benefit or cost from consuming one more unit of a good or service. 💡 This is where the magic happens!
#Example: Pizza 🍕
- Total Benefit: Eating 5 slices of pizza gives you 15 utils (units of satisfaction).
- Total Cost: Those 5 slices cost you
- Marginal Cost: Each additional slice costs you4 (constant marginal cost).
Utils are just imaginary units of utility or satisfaction. They help us quantify how much we like something.
#Diminishing Marginal Utility
- As you consume more of a good, the additional satisfaction you get from each additional unit decreases. This is why the 10th slice of pizza isn't as good as the first.
- Eventually, you can even reach negative marginal utility where you're worse off by consuming more.
Think of it like this: the first bite of a delicious burger is amazing, but the 10th bite? Not so much. That’s diminishing marginal utility in action!
#4. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
- Definition: As you consume more of a good or service, the additional satisfaction from each extra unit eventually declines.
- Real-World Impact: Explains why we don't consume infinite amounts of anything. There's a point where it's just not worth it.
#5. The Cost-Benefit Maximizing Principle
- Goal: To maximize total benefit (or surplus).
- Marginal Surplus: The difference between marginal benefit (MB) and marginal cost (MC).
- Rule: Total benefit is maximized when MB = MC. This is the sweet spot!
#Scenarios
- MB > MC: Keep consuming! You're still gaining more than you're losing.
- MB = MC: You've hit the maximum benefit. Stop here!
- MB < MC: You're losing benefit by consuming more. Cut back!
Remember, the goal is to find the point where MB = MC. If there's no exact point, consume up to, but not including, where MB < MC.
#Visualizing MB and MC
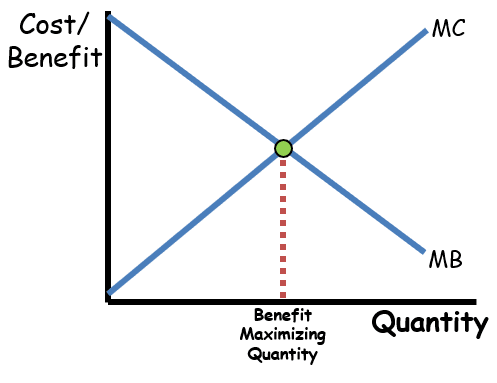
Source: ReviewEcon
- To the left of the intersection, MB > MC. To the right, MB < MC.
- The optimal quantity is where the curves intersect (MB = MC).
Understanding the relationship between marginal benefit and marginal cost is crucial for maximizing utility and is a frequent topic on the AP exam.
#6. Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics
- Explicit vs. Implicit Costs: Know the difference and how they impact decision-making.
- Marginal Analysis: Understand marginal benefit, marginal cost, and how they relate to total benefit.
- Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: Be able to explain it and give examples.
- Cost-Benefit Maximizing Principle: Know that MB = MC is the key to maximizing benefit.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Expect questions that ask you to identify explicit vs. implicit costs, calculate opportunity costs, and apply marginal analysis.
- Free Response: Be prepared to draw and interpret graphs of marginal benefit and marginal cost, and explain how to maximize total benefit.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back to it later.
- Common Pitfalls: Watch out for tricky wording in questions. Make sure you understand what the question is asking before you answer.
- Strategies: Draw diagrams to help you visualize concepts. Use real-world examples to make the concepts more concrete.
Students often confuse total benefit with marginal benefit. Remember, marginal benefit is the additional benefit from one more unit.
#7. Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
After graduating high school, Billy decided to enroll in a two-year program at the local community college rather than to accept an internship that offered a salary of 5,000, the annual opportunity cost of attending the community college is: (A) 10,000 (C) 20,000 (E)
Answer: (D)20,000
Explanation: Opportunity cost includes both explicit and implicit costs. The 5,000 in tuition and fees is the explicit cost of going to the community college.
-
All of the following are included in computing the opportunity cost of attending college EXCEPT: (A) interest paid on student loans (B) wages the student gave up to attend college (C) money spent on books and supplies (D) money spent on college tuition (E) money spent on clothing expenses
Answer: (E)
Explanation: No matter what decision you make, you will always have clothing expenses.
-
Sylvia works part-time at a local convenience store and earns 100, but Sylvia was able to get a discounted price of 75 (B) 135 (D) 175
Answer: (C)
Explanation: Sylvia would have earned60 from working for 5 hours (implicit cost). She also spent 75 on the ticket (explicit cost). 60 + 75 = 135. ### Free Response Question
Jane’s marginal benefit per day from drinking Pepsi is given in the table below. The table shows that she values the first Pepsi she drinks at1.25, the second at 1.00, how many should Jane drink?

(a) How many Pepsis should Jane drink to maximize her total benefit? Explain your reasoning.
(b) Calculate Jane's total benefit from consuming the optimal number of Pepsis.
(c) Calculate Jane's total cost from consuming the optimal number of Pepsis.
(d) Calculate Jane's total surplus (total benefit - total cost) from consuming the optimal number of Pepsis.
Answer Key:
(a) Jane should drink 3 Pepsis. This is because the marginal benefit of the 3rd Pepsi (1.00), which is the price of a Pepsi. For the first Pepsi, Jane gains 0.20. For the third,
(b) Total benefit =1.25 + 1.00 =
(c) Total cost = 3 Pepsis *1.00/Pepsi =
(d) Total surplus = Total benefit - Total cost =3.45 - 0.45
You've got this! Remember to stay calm, use your strategies, and trust in your preparation. Good luck on your AP Microeconomics exam! 🎉
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





