Price Elasticity of Demand
Nancy Hill
8 min read
Study Guide Overview
This guide covers Price Elasticity of Demand (PED), including its meaning as responsiveness to price changes. It explains how to calculate PED using the formula and percentage changes in quantity demanded and price. The guide details the five types of elasticity, from perfectly inelastic to perfectly elastic, and illustrates them with examples. It also explains the total revenue test to determine elasticity and provides practice questions, including multiple-choice and free-response questions, along with a scoring rubric.
#AP Microeconomics: Price Elasticity of Demand - Your Ultimate Guide 🚀
Hey there, future AP Micro ace! Let's break down Price Elasticity of Demand (PED). This is a huge topic, so let's make sure you've got it down cold. Think of this as your pre-game huddle before the big exam. Let’s get started!
#What is Price Elasticity of Demand?
At its core, PED measures how sensitive consumers are to price changes. It's all about understanding how much the quantity demanded of a good changes when its price changes. Are people super responsive or not so much? That's what PED tells us.
Think of elasticity as responsiveness. How much does quantity demanded react to a price change?
Imagine two friends, Harry and Sally, buying turkey sandwiches. If a price increase makes Harry drastically reduce his sandwich purchases, but Sally barely changes her buying habits, Harry is more price-sensitive (his demand is more elastic), while Sally is less so (her demand is more inelastic).

#Calculating Price Elasticity of Demand
Here’s the formula:
E_d = \frac{%\Delta Q_d}{%\Delta P}
Where:
- is the price elasticity of demand coefficient
- is the percentage change in quantity demanded
- is the percentage change in price
PED = % Change in Quantity / % Change in Price. Remember, quantity on top, price on the bottom. Quick way to remember it!
Since demand curves are downward sloping, will usually be negative. We often use the absolute value to focus on the magnitude of the responsiveness. Let's calculate Harry's PED:
- Initial Quantity (Q1): 5 sandwiches
- New Quantity (Q2): 1 sandwich
- %ΔQd: ((1-5)/5) * 100 = -80%
- Initial Price (P1):
- New Price (P2):15
- %ΔP: ((15-10)/10) * 100 = 50%
E_d = \frac{-80%}{50%} = -1.6
Harry's PED is -1.6 (or 1.6 in absolute value), indicating that his demand is relatively elastic.
#Types of Elasticity
There are 5 main types of elasticity, each describing a different level of consumer responsiveness:
#1. Perfectly Inelastic Demand
- = 0
- Quantity demanded does not change regardless of price changes. Think of life-saving medicines like insulin or basic necessities. 📈
#2. Relatively Inelastic Demand
- 0 < < 1
- Quantity demanded is not very responsive to price changes. Example: gasoline. People need it, even if the price goes up. 🚗
#3. Unit Elastic Demand
- = 1
- Quantity demanded changes proportionally to price changes. Total revenue is maximized at this point. ⚖️
#4. Relatively Elastic Demand
- 1 < < ∞
- Quantity demanded is highly responsive to price changes. Think of leisure activities like concerts or movies. 🎬
#5. Perfectly Elastic Demand
- = ∞
- Quantity demanded is infinitely responsive to price changes. This is more of a theoretical concept, but think of goods with many perfect substitutes. 🛒
Perfectly inelastic and perfectly elastic are theoretical extremes. Real-world goods usually fall somewhere in between.
Here's a visual to help:
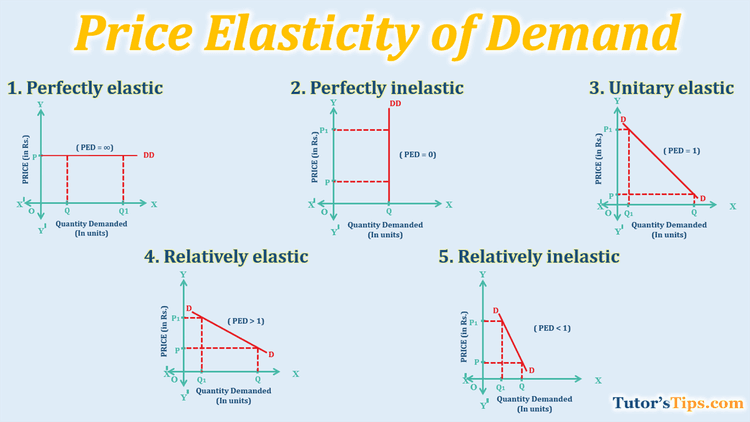
Don't confuse elasticity with the slope of the demand curve. Elasticity changes along a demand curve because it's based on percentage changes, not absolute changes. Even a straight-line demand curve will have different elasticities at different points.

#The Total Revenue Test
Total Revenue (TR) is the amount of money a business brings in: TR = P * Q.
The total revenue test helps determine elasticity by looking at how total revenue changes with price changes:
- Elastic Demand:
- Price ⬆️, TR ⬇️
- Price ⬇️, TR ⬆️
- Inelastic Demand:
- Price ⬆️, TR ⬆️
- Price ⬇️, TR ⬇️
- Unit Elastic Demand:
- Price ⬆️ or ⬇️, TR stays the same
Elastic: Think of a rubber band – it stretches a lot (quantity changes a lot with price). Inelastic: Think of a brick – it doesn't change shape much (quantity doesn't change much with price).

#Sample Problem

The total revenue test is a quick way to determine elasticity without calculating the coefficient. It's super useful on the exam when time is tight.
Firms use this test to make strategic pricing decisions. If demand is elastic, they need to be careful about raising prices, as it could reduce their total revenue.
#Final Exam Focus
Okay, let's get down to brass tacks. Here’s what you really need to know for the exam:
- Understand the PED formula and how to calculate it. Practice a few examples!
- Know the 5 types of elasticity and what they mean in real-world scenarios. Think of examples for each.
- Master the total revenue test and how it relates to elasticity. This is a quick way to answer questions on the exam.
- Recognize that elasticity varies along a demand curve. Don't fall for the trap of thinking slope = elasticity.
- Connect PED to real-world examples: Think about how businesses use elasticity to set prices.
Price elasticity of demand is a high-value topic. It often appears in both multiple-choice and free-response questions. Make sure you understand it thoroughly.
#Last-Minute Tips:
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back later.
- Common Pitfalls: Be careful with percentage changes. Make sure you're using the correct base when calculating them.
- FRQs: Clearly label your graphs and explain your reasoning step-by-step. Points are awarded for understanding, not just the final answer.
#Practice Questions
Let's test your knowledge with some practice questions.
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions
-
If the price of a good increases by 10% and the quantity demanded decreases by 5%, the demand for the good is: (A) Perfectly elastic (B) Elastic (C) Unit elastic (D) Inelastic (E) Perfectly inelastic
-
A perfectly inelastic demand curve is: (A) Horizontal (B) Vertical (C) Downward sloping (D) Upward sloping (E) A curve with a slope of 1
-
If a firm increases the price of its product and its total revenue decreases, the demand for the product is: (A) Perfectly elastic (B) Elastic (C) Unit elastic (D) Inelastic (E) Perfectly inelastic
Free Response Question
Assume that a local coffee shop is considering changing the price of its signature latte. Currently, they sell 200 lattes per day at a price of 6, at which they estimate they would sell 150 lattes per day.
(a) Calculate the price elasticity of demand for lattes using the midpoint formula. (b) Is the demand for lattes elastic, inelastic, or unit elastic? Explain. (c) Should the coffee shop increase the price of lattes? Explain using the total revenue test. (d) Draw a graph showing the demand curve and the total revenue at both price points. Label the graph clearly.
Scoring Rubric
(a) (3 points) * 1 point for correctly calculating the percentage change in quantity: ((150-200)/((150+200)/2)) * 100 = -28.57% * 1 point for correctly calculating the percentage change in price: ((6-5)/((6+5)/2)) * 100 = 18.18% * 1 point for correctly calculating the price elasticity of demand: -28.57/18.18 = -1.57
(b) (2 points) * 1 point for stating that the demand is elastic * 1 point for explaining that the absolute value of the elasticity coefficient is greater than 1
(c) (2 points) * 1 point for stating that the coffee shop should not increase the price * 1 point for explaining that the total revenue will decrease (TR at 6 = 900) because demand is elastic
(d) (3 points) * 1 point for correctly labeling the axes (Price on the vertical, Quantity on the horizontal) * 1 point for correctly plotting the two points (200, 5) and (150, 6) * 1 point for showing the total revenue at both points, either by shading the areas or indicating the TR values next to the points
Alright, you've got this! Go into that exam with confidence and show them what you've learned. You're going to do great!
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





