Vector Fields
Daniel Miller
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers circular motion and vector fields, focusing on Uniform Circular Motion (UCM). Key concepts include defining and visualizing vector fields, understanding forces in UCM (centripetal force, tension, friction, gravity, normal force), and differentiating between centripetal and centrifugal forces. It also covers the centripetal force equation and briefly touches on gravitational vector fields. Practice questions and exam tips are included.
#AP Physics 1: Circular Motion & Vector Fields 🚀
Hey there, future physics pro! Let's get you prepped for the AP exam with a super-focused review of circular motion and vector fields. This is your go-to guide for tonight – let's make it count!
#
Vector Fields: Visualizing Forces
A vector field is like a map of forces, showing the direction and strength of a force at different points in space. Think of it as arrows all over the place, each one telling you what a force would do at that spot.
- Definition: A vector field assigns a vector to each point in space.
- Visualization: Imagine arrows with different lengths (magnitude) and directions at every point.

Caption: A vector field showing the tangential velocity of an object in circular motion.
#
Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
#What is UCM?
Uniform circular motion happens when an object moves in a circle at a constant speed. Even though the speed is constant, the object is still accelerating because its direction is always changing. 🔄
- Constant Speed, Changing Velocity: Speed is constant, but velocity changes due to direction change.
- Acceleration: Always present in UCM due to the change in direction.
#Forces in UCM
In UCM, you'll usually encounter forces like tension, friction, gravity, and normal forces. These forces are the cause of the centripetal force.
Centripetal force is NOT a new force. It's just the net force that points towards the center of the circle, causing the circular motion. Don't draw it on your free-body diagrams!

Caption: Centripetal acceleration and force point towards the center of the circle, while velocity is tangent to the circle.
#Key Directions
- Centripetal Acceleration: Always points towards the center of the circle.
- Centripetal Force: Also points towards the center.
- Velocity: Always tangent to the circle.
Forces pointing towards the center are considered positive (+), and forces pointing away are negative (-). Tangential forces (like velocity) don't contribute to the net centripetal force.
#Centrifugal vs. Centripetal
- Centripetal: Center-seeking. It's a real force that causes circular motion.
- Centrifugal: Center-fleeing. It's an apparent force felt in a rotating frame, not a real force.
Remember: CentriPETAL is like a petal of a flower, always pointing towards the center. CentriFUGAL is like a fugitive, trying to escape the center.
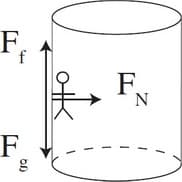
Caption: In this free-body diagram, there's no centrifugal force. Static friction is what keeps the person from sliding down.
#Centripetal Force Equation
Where:
- = Centripetal Force (N)
- m = mass (kg)
- v = velocity (m/s)
- r = radius (m)
Remember, this equation is just Newton's second law () with the centripetal acceleration () plugged in.
#Vector Fields and Gravity
While AP Physics 1 doesn't dive deep into gravitational vector fields, you should understand how vectors represent gravitational forces between two objects.

Caption: The vectors show the gravitational attraction between the Earth and the Moon.
#Key Points
- Force Direction: Vector pointing left represents the gravitational force of Earth on the Moon (pulling it towards Earth). Vector pointing right represents the gravitational force of the Moon on the Earth (pulling it towards the Moon).
- Center of Mass: Distances are calculated between the centers of mass of the objects.
- Magnitude and Direction: Vectors show both the strength and direction of the gravitational force.
#Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics
- Uniform Circular Motion: Understand the concepts of centripetal force and acceleration.
- Vector Fields: Be able to interpret vector representations of forces.
- Free-Body Diagrams: Practice drawing accurate diagrams for circular motion scenarios.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Conceptual questions about centripetal vs. centrifugal force, direction of acceleration, and forces in UCM.
- Free Response: Problems involving calculations of centripetal force, application of Newton's laws to circular motion, and analysis of scenarios with friction, tension, and gravity.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on one question. Move on and come back if you have time.
- Common Pitfalls: Avoid confusing centripetal force with a separate force. Remember it's the net force.
- Strategies: Draw free-body diagrams for every force problem. Clearly show your work for FRQs.
#Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
A car is moving at a constant speed around a circular track. Which of the following statements is true? (A) The car's velocity is constant. (B) The car's acceleration is zero. (C) The car's acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle. (D) The car's acceleration is directed tangent to the circle.
-
A ball is swung in a vertical circle at a constant speed. At which point in the circle is the tension in the string the greatest? (A) At the top of the circle. (B) At the bottom of the circle. (C) At the sides of the circle. (D) The tension is the same at all points.
-
A satellite is orbiting the Earth in a circular path. What force provides the centripetal force necessary for this motion? (A) The normal force (B) The gravitational force (C) The tension force (D) The frictional force
#Free Response Question
A 2.0 kg toy car moves with a constant speed of 3.0 m/s in a horizontal circle of radius 1.5 m.
(a) Calculate the centripetal acceleration of the car. (2 points) (b) Calculate the centripetal force acting on the car. (2 points) (c) If the car is being held in its circular path by a string, what is the tension in the string? (2 points) (d) Draw a free-body diagram of the car, indicating all forces acting on it. (2 points) (e) If the string breaks, describe the subsequent motion of the car. (2 points)
Answer Key:
(a)
- 1 point for correct formula
- 1 point for correct answer
(b)
- 1 point for correct formula
- 1 point for correct answer
(c) The tension in the string provides the centripetal force, so T = Fc = 12 N.
- 2 points for correct answer (1 point for understanding that tension provides the centripetal force and 1 point for correct answer)
(d)
- 1 point for correct normal force
- 1 point for correct gravitational force (No centripetal force on the free body diagram)
(e) The car will move in a straight line tangent to the circle at the point where the string broke.
- 2 points for correct answer
You've got this! Let's ace that exam! 🌟
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





