The Great Depression
Daniel Miller
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers the Great Depression, focusing on its causes (BOPS: Bank Failures, Overproduction, Purchasing Reduction, Stock Market Crash), impact (Dust Bowl, unemployment), Hoover's response (limited intervention, Bonus March), and the election of FDR (New Deal). It also includes practice questions covering multiple-choice, short answer, and free response formats and emphasizes exam strategies.
#AP US History: The Great Depression - Night Before Review
Hey! Let's get you prepped and confident for your AP US History exam. We're focusing on the Great Depression, a huge topic, so let's dive in with a clear, organized approach. Remember, you've got this! 💪
#1. Introduction to the Great Depression
- The Great Depression was the most severe economic downturn in US history. 📉
- High unemployment (peaked at ~25%) and widespread desperation were hallmarks of this era.
- Understanding its causes and impacts is crucial for the exam. Let's get started!
The Great Depression is a high-value topic on the AP exam. Expect multiple-choice and free-response questions that test your understanding of its causes, effects, and the government's response.
#2. Causes of the Great Depression
Let's use the acronym BOPS to help remember the main causes:
- B - Bank Failures 🏦: Banks ran out of money due to mass withdrawals.
- O - Overproduction 🏭: Companies and farmers produced too many goods, exceeding demand.
- P - Purchasing Reduction 📉: Consumers reduced spending, further decreasing demand.
- S - Stock Market Crash 💥: The 1929 crash triggered a downward economic spiral.
BOPS - Banks, Overproduction, Purchasing, Stock. This will help you remember the four major causes of the Great Depression!
#2.1 The Stock Market Crash
-
The Roaring Twenties featured unregulated credit and margin buying. 💸
-
Margin buying: Investors borrowed money to buy stocks, inflating their value.
-
Black Tuesday (October 29, 1929): The stock market crashed, triggering a massive sell-off.
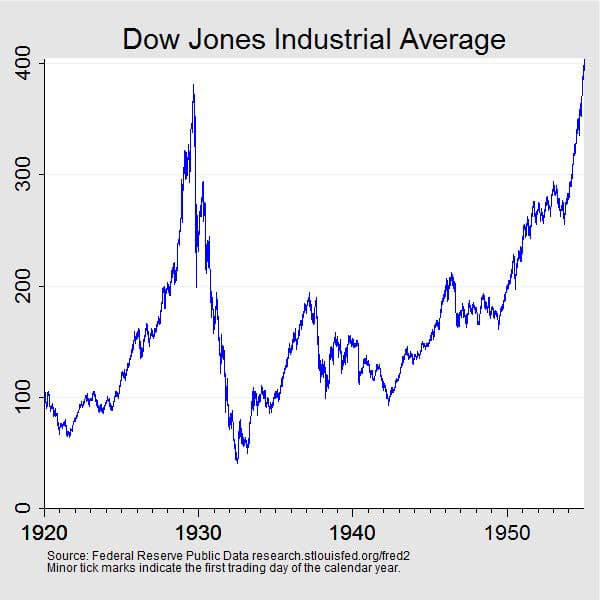
Caption: The Dow Jones Industrial Average, 1920 to 1955. Note the sharp increase through the 20s and then the absolute CRASH in 1929.
#2.2 Bank Failures
-
Lack of regulation and risky loans made banks vulnerable. 🏦
-
Run on the bank: Mass withdrawals caused banks to collapse.
-
By 1933, many states had no banks left. 😳
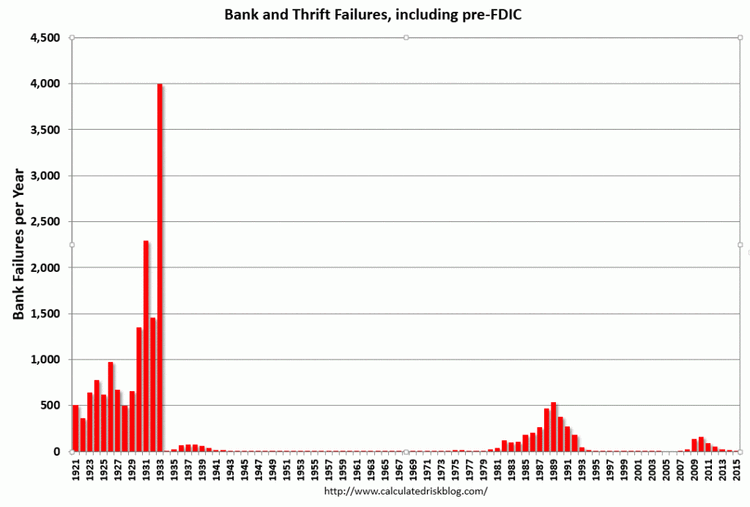
Caption: Bank failures in the US between 1921 and 2015. Note the spike during the Great Depression.
Remember that the stock market crash and bank failures were not isolated events. They were interconnected and exacerbated each other, leading to a full-blown economic crisis.
#2.3 The Dust Bowl
- Overproduction and poor farming practices led to the Dust Bowl. 🌪️
- High winds, low rainfall, and soil erosion devastated the agricultural sector.
- Okies: Farmers migrated to California in search of work.
#3. Hoover's Response
-
The Federal Reserve tightened the money supply, worsening the crisis. 😬
-
Hawley-Smoot Tariff: Raised taxes on imports, leading to a decline in global trade.
-
President Herbert Hoover was criticized for his limited response.
- He tried limited public works and voluntary business deals.
- Homeless people lived in Hoovervilles.

Caption: Homeless people lived in shantytowns called "Hoovervilles" during the Great Depression.
Don't assume Hoover did nothing. He did try some measures, but they were not enough to combat the severity of the Depression. His policies were based on the limited government approach of the time.
#3.1 Bonus March
- WWI veterans marched on Washington demanding early payment of their bonus. 🪖
- Hoover refused, and the army forcibly removed the veterans.
#4. Election of 1932
- Franklin Delano Roosevelt (FDR) won the election in a landslide. 🎉
- FDR promised a New Deal to address the crisis.
- His famous quote: "The only thing we have to fear is fear itself."
- First Hundred Days: FDR proposed numerous pieces of legislation to combat the Depression.
FDR's "First Hundred Days" is a key concept. It refers to the initial period of his presidency when many significant New Deal programs were enacted. Remember this when you see questions about the early New Deal.
#5. Final Exam Focus
- High-Priority Topics:
- Causes of the Great Depression (BOPS)
- Impact of the Stock Market Crash and Bank Failures
- The Dust Bowl and its effects
- Hoover's response and the Bonus March
- The Election of 1932 and the beginning of the New Deal
- Common Question Types:
- Multiple Choice: Cause-and-effect relationships, key events, and political figures.
- Short Answer: Explaining the impact of specific events or policies.
- Free Response: Analyzing the causes of the Depression or the effectiveness of government responses.
- Last-Minute Tips:
- Time Management: Scan questions carefully and prioritize those you know best.
- Common Pitfalls: Avoid oversimplifying complex issues and make sure to provide evidence in your answers.
- Strategies: Connect different units where possible, as AP questions often combine multiple concepts.
#6. Practice Questions
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following was NOT a major cause of the Great Depression? (A) Overproduction of goods (B) Bank failures (C) Increased government spending (D) The Stock Market Crash
-
The Dust Bowl primarily affected which region of the United States? (A) The Northeast (B) The Southeast (C) The Great Plains (D) The Pacific Northwest
-
What was the purpose of the Hawley-Smoot Tariff? (A) To increase international trade (B) To protect American industries (C) To lower the prices of goods (D) To regulate the stock market
Short Answer Question
- Briefly explain how the stock market crash of 1929 contributed to the Great Depression. Include at least two specific examples.
Free Response Question
Analyze the causes of the Great Depression. In your response, be sure to discuss economic factors, social factors, and governmental policies. (6 points)
- Point 1: Identification of one economic factor (e.g., overproduction, stock market speculation).
- Point 2: Explanation of the economic factor's impact on the Depression.
- Point 3: Identification of one social factor (e.g., Dust Bowl, unemployment).
- Point 4: Explanation of the social factor's impact on the Depression.
- Point 5: Identification of one governmental policy (e.g., Hawley-Smoot Tariff, Federal Reserve actions).
- Point 6: Explanation of the governmental policy's impact on the Depression.
Alright, you've reviewed the key points of the Great Depression. You're now equipped with the knowledge and strategies to tackle those AP questions. Go get 'em! 🚀
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





