The African Continent: A Varied Landscape
Ryan Lee
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This AP African American Studies study guide covers African geography's influence on history and culture, focusing on climate zones (desert, semiarid, savanna, tropical rainforest, Mediterranean), major waterways (Red Sea, Mediterranean Sea, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Niger, Congo, Zambezi, Orange, and Nile Rivers), and how these factors shaped settlement patterns, trade routes, and the development of early societies. It emphasizes the relationship between climate diversity and trade opportunities, provides practice questions, and offers exam tips.
#AP African American Studies: Ultimate Study Guide
Hey! Let's get you totally prepped for the AP exam. This guide is designed to be your best friend the night before the test. We'll make sure everything clicks, and you'll feel confident and ready to go! Let's dive in!
#🌍 Africa's Geography: Setting the Stage
Africa's diverse geography is not just a backdrop; it's a key player in shaping its history, cultures, and economies. Understanding this is crucial for the exam.
#🌡️ Climate Zones
Africa’s landscape is incredibly varied, leading to five distinct climate zones:
- Desert: Think Sahara – scorching heat, very little rain. 🏜️
- Semiarid: Like the Sahel, a bit more rain than the desert but still pretty dry.
- Savannah: Grasslands with scattered trees and seasonal rain. Perfect for those iconic African landscapes! 🦁
- Tropical Rainforest: Near the equator, lots of rain, dense forests, and crazy biodiversity. 🌳
- Mediterranean: Mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, found in parts of North Africa and the southern tip. ☀️
#🌊 Borders and Waterways
Africa's borders are defined by its surrounding bodies of water:
- Red Sea: Separates Africa from the Middle East.
- Mediterranean Sea: Northern border.
- Atlantic Ocean: Western border.
- Indian Ocean: Eastern border.
Major Rivers:
-
Niger River: West Africa 🌊
-
Congo River: Central Africa 🏞️
-
Zambezi River: Southern Africa 🏞️
-
Orange River: Southern Africa 🏞️
-
Nile River: Longest river in the world, flowing from East Africa to the Mediterranean. 🏞️
Remember the rivers with Nice Cats Zoning Out Nearby: Niger, Congo, Zambezi, Orange, Nile
#🏘️ How Landscape Shapes Settlement
#🚢 Early Societies and Connections
- Proximity to the Red Sea, Mediterranean Sea, and Indian Ocean was a game-changer for early societies.
- Coastal access meant easy fishing and trade, which led to economic growth and cultural exchange. Think of ancient Egypt, Punt, and the Swahili city-states. 💡
#🏘️ Population Centers
The Sahel and savannah became major population hubs due to:
- Water routes: Like the Niger River and Lake Chad, which made trade and travel easier.
- Fertile soils: Great for farming crops like sorghum, millet, and rice.
- Trade connections: These areas linked the Sahara to the tropical regions, allowing trade in gold, salt, and ivory.
Key population centers include:
- Timbuktu and Gao (Mali Empire)
- Koumbi Saleh (Ghana Empire)
- Kanem-Bornu (near Lake Chad)
#💰 Climate and Trade Opportunities
Africa's diverse climates led to varied trade opportunities:
-
Deserts/Semiarid: Nomadic herders, salt production (Tuareg, Berber).
-
Sahel: Livestock trading (Fulani).
-
Savannah: Grain crops (Hausa city-states).
-
Tropical Rainforests: Kola nuts, yams, and gold (Akan, Ashanti Kingdom).
Remember: Climate diversity = trade diversity! Each region had its specialty, leading to vibrant trade networks.
#🗺️ Visual Aid: Climate Regions of Africa
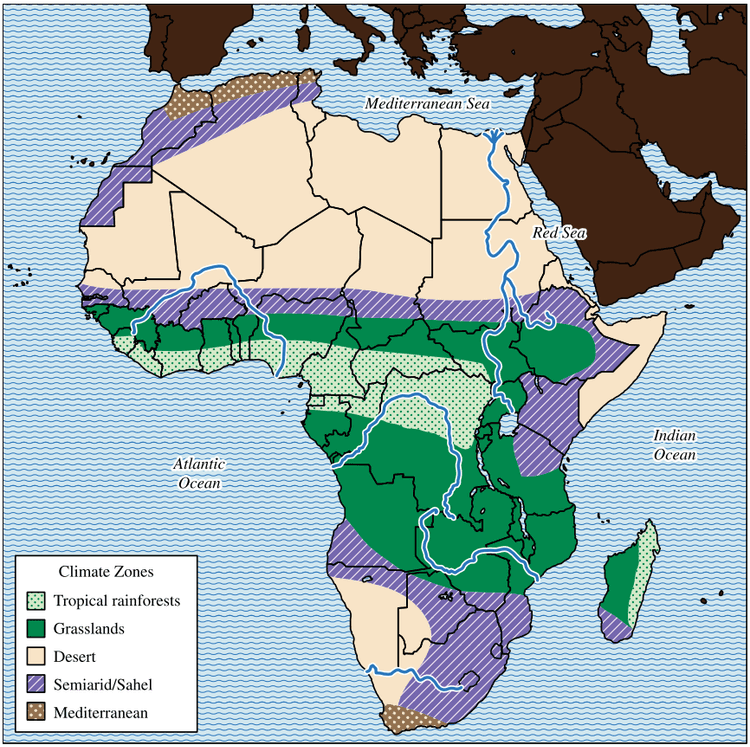
This map is super helpful for understanding how different climate zones influenced settlement, agriculture, and resource distribution. It’s a visual reminder of how much geography has shaped African societies. Make sure to use this map to help you understand the different regions and how they are connected.
When you see a map on the exam, take a moment to analyze it. What patterns do you notice? How does it connect to the question being asked?
#🎯 Final Exam Focus
Okay, here’s what to really focus on:
-
Geographic Impact: How did climate and landscape affect settlement, trade, and cultural development? (See: Africa's Geography, Landscape Effects on Settlement)
-
Trade Networks: Understand the major trade routes and the goods that were exchanged. (See: Climate and Trade Opportunities)
-
Key Civilizations: Know the major societies and their connections to geography (See: Early Societies and Connections, Population Centers)
Geography is foundational! Questions often link it to other topics like economics, culture, and politics. Master this, and you'll be in great shape.
#⏰ Time Management Tips
- Scan questions first: Identify the main topic and what the question is asking.
- Prioritize: Answer questions you know well first.
- Don't get stuck: If a question is taking too long, move on and come back later.
#⚠️ Common Pitfalls
- Not linking geography to human impact: Remember, it's not just about memorizing locations but understanding how they affected people.
- Ignoring the map: Maps are there for a reason! Use them to your advantage.
- Rushing through questions: Take a breath and read carefully.
#💪 Strategies for Challenging Questions
- Break it down: Complex questions often have multiple parts. Tackle each one step-by-step.
- Use evidence: Always back up your answers with specific examples.
- Connect the dots: Look for links between different units and concepts.
#📝 Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the impact of the Niger River on West African societies?
(A) It served as a major barrier to trade and communication. (B) It facilitated the movement of people and goods, supporting trade and communication. (C) It led to the development of isolated and independent communities. (D) It caused frequent flooding, making agriculture impossible.
-
The varied climate zones of Africa had the greatest impact on the:
(A) Development of a single unified culture across the continent. (B) Creation of diverse economic opportunities and trade networks. (C) Establishment of large-scale industrial production centers. (D) Adoption of a singular political system by all African societies.
#Short Answer Question
Briefly explain how the geographic features of Africa, such as rivers and climate zones, influenced the development of early societies and trade networks. Provide at least two specific examples from the text.
#Free Response Question
Analyze the ways in which the diverse climate zones of Africa have shaped the economic activities and population distribution across the continent. In your response, be sure to:
- Identify and explain at least three distinct climate zones.
- Describe the economic activities associated with each climate zone.
- Discuss how these climate zones influenced population settlement patterns.
Scoring Breakdown:
- Identification of climate zones (3 points): 1 point for each correctly identified climate zone (e.g., desert, savanna, rainforest).
- Description of economic activities (3 points): 1 point for each economic activity correctly linked to a climate zone (e.g., nomadic herding in deserts, grain cultivation in savannahs, gold trade in rainforests).
- Discussion of population patterns (3 points): 1 point for each well-explained link between a climate zone and population settlement (e.g., higher populations in savannahs due to fertile soil, coastal settlements due to trade opportunities).
- Analysis and Synthesis (1 point): For a response that demonstrates a clear understanding of the interconnectedness of climate, economy, and population patterns, and provides specific examples from the text.
You've got this! Go get that 5! 🎉
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





