Slave Auctions and the Domestic Slave Trade
Maya Hall
9 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers the brutal realities of slave auctions and the domestic slave trade, including the nature of slave auctions, African American abolitionist writings countering benign slavery claims, and the cotton industry's impact on family displacement. It analyzes primary sources like Twelve Years a Slave and a Charleston Courthouse broadside. The guide emphasizes the Second Middle Passage, provides practice MCQs and FRQs, and offers exam tips focusing on high-priority topics like the domestic slave trade's impact and the role of cotton.
#AP African American Studies: The Night Before Review 🚀
Hey! Let's make sure you're feeling confident and ready to crush this exam. We've got a lot to cover, but we'll make it engaging and easy to remember. Think of this as your ultimate cheat sheet, not just a review. Let's get started!
#1. The Brutal Reality of Slave Auctions and the Domestic Slave Trade 💔
#
Nature of Slave Auctions
Slave auctions were not just business transactions; they were sites of extreme violence and dehumanization. This is a key concept for both MCQs and FRQs.
- Assault on Enslaved People:
- Enslavers used law and white supremacy to inflict physical, mental, and spiritual violence. 😠
- Auctions were a stage for brutal punishments, like whippings, designed to break spirits and deter resistance. 🪢
- Families were torn apart, causing deep psychological trauma. 💔
- Enslaved people were treated as commodities, stripping them of their humanity. 📦
#
African American Abolitionist Writings
- Literary Genres for Auction Experiences:
- Narratives: Firsthand accounts of the horrors of auctions. ✍️
- Example: Frederick Douglass's Narrative vividly portrays the anguish of family separation. 📖
- Poetry: Expressed raw emotions and psychological impact. 📜
- Example: Frances Ellen Watkins Harper's "The Slave Auction" captures despair and helplessness. 😢
- Plays: Brought the horrors of auctions to life, fostering empathy. 🎭
- Example: William Wells Brown's The Escape dramatizes the desperation to avoid being sold. 🏃🏾
- Narratives: Firsthand accounts of the horrors of auctions. ✍️
- Countering Claims of Benign Slavery:
- Abolitionists used their experiences to debunk the myth of benevolent slavery. 🙅🏾u200d♂️
- They exposed the brutality and inhumanity of the system. 💥
- Their writings challenged the idea that enslavers had the best interests of the enslaved at heart. ❤️u200d🔥
- They aimed to garner support for the abolitionist movement by appealing to shared humanity. 🤝
#
Cotton Industry and Family Displacement
- Post-1808 Enslaved Population Growth:
- The ban on the transatlantic slave trade led to increased reliance on domestic reproduction. 🤰🏾
- Enslaved women's reproductive capacity was exploited. 😥
- Children were seen as future laborers and valuable assets. 👶🏽
- The domestic slave trade thrived as a result. 📈
- Slave-Cotton System in Lower South:
- The lower South's economy was based on cotton, requiring a large enslaved workforce. 🧑🏿u200d🌾
- Enslaved people were essential commodities, their value tied to cotton profitability. 💰
- The demand for labor fueled the domestic slave trade. 🚂
- Expansion of cotton led to forced relocation and sale of families. 💔
- Domestic Slave Trade Relocation:
- The cotton boom led to a massive forced migration from the upper to the lower South. 🗺️
- Enslaved people were sold to traders and transported to cotton plantations. 🚚
- This trade was highly profitable for enslavers and traders. 🤑
- Enslaved people were forced to march in coffles, enduring immense hardship. ⛓️
- Families and communities were shattered. 💔
- Second Middle Passage Displacement:
- The forced migration of over one million enslaved people is known as the "Second Middle Passage." 🚢
- More people were displaced than during the original Middle Passage. 🤯
- Enslaved people endured immense physical, psychological, and emotional trauma. 😞
- This was the largest forced migration in American history. 😥
Think of the 'Second Middle Passage' as the internal version of the transatlantic journey, but within the US. It highlights the sheer scale of forced migration and the brutality of the domestic slave trade. 🚢➡️ 🇺🇸
#2. Required Sources: Deep Dive 🧐
#Excerpt from Twelve Years a Slave by Solomon Northup, 1853
"She wanted to be with her children, she said, the little time she had to live. All the frowns and threats of Freeman, could not wholly silence the afflicted mother. She kept on begging and beseeching them, most piteously not to separate the three. Over and over again she told them how she loved her boy. A great many times she repeated her former promises - how very faithful and obedient she would be; how hard she would labor day and night, to the last moment of her life, if he would only buy them all together. But it was of no avail; the man could not afford it. The bargain was agreed upon, and Randall must go alone. Then Eliza ran to him; embraced him passionately; kissed him again and again; told him to remember her - all the while her tears falling in the boy’s face like rain.
Freeman damned her, calling her a blubbering, bawling wench, and ordered her to go to her place, and behave herself; and be somebody. He swore he wouldn’t stand such stuff but a little longer. He would soon give her something to cry about, if she was not mighty careful, and that she might depend upon.
The planter from Baton Rouge, with his new purchases, was ready to depart.
“Don’t cry, mama. I will be a good boy. Don’t cry,” said Randall, looking back, as they passed out of the door.
What has become of the lad, God knows. It was a mournful scene indeed. I would have cried myself if I had dared."
- Key Takeaways:
- Firsthand account of the brutal realities of slavery. 😥
- Highlights the dehumanizing nature of the system. 💔
- Shows the constant threat of kidnapping faced by free Black Americans. ⚠️
- Illustrates the complicity of Northern and Southern institutions. 🏛️
- Showcases the resilience of those trapped within the system. 💪🏾
#Broadside for an Auction of Enslaved Persons at the Charleston Courthouse, 1859
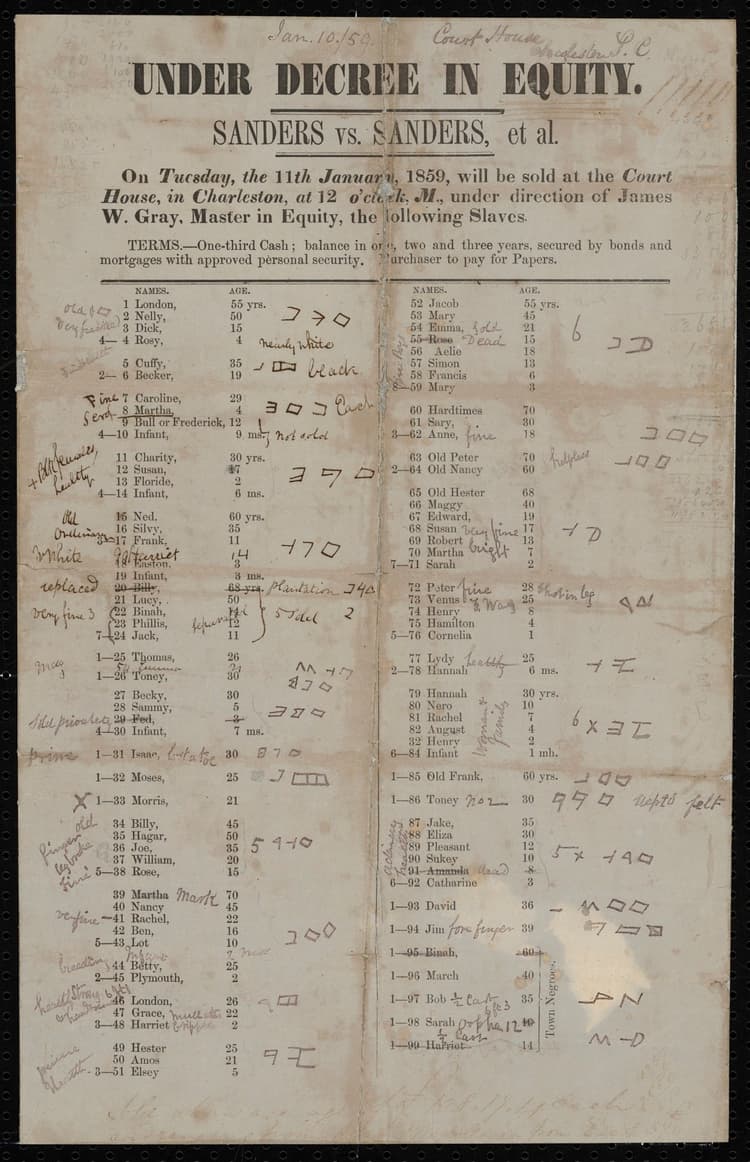
- Key Takeaways:
- Tangible evidence of the commodification of human beings. 🏷️
- Represents the economic foundation of slavery. 💰
- Highlights the institutionalized racism and dehumanization of the system. 😠
- Offers a direct connection to the lived experiences of enslaved people. 🔗
- Illustrates the trauma of family separation and denial of human rights. 💔
Remember, primary sources like these are gold on the AP exam. Use them to support your arguments in FRQs. 🥇
#3. Final Exam Focus 🎯
#
Highest-Priority Topics
- The domestic slave trade and its impact on families and communities.
- The role of cotton in fueling the demand for enslaved labor.
- The experiences of enslaved people at auctions and during the Second Middle Passage.
- The significance of abolitionist writings in exposing the horrors of slavery.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs): Focus on understanding the causes and effects of the domestic slave trade and the experiences of enslaved people.
- Short Answer Questions (SAQs): Be prepared to analyze primary sources and explain the significance of events and movements.
- Free Response Questions (FRQs): Practice writing essays that connect multiple themes and use evidence to support your claims.
Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back to it later. ⏰
#Common Pitfalls
- Not connecting events to broader themes.
- Failing to use evidence from the provided sources in FRQs.
- Overlooking the psychological impact of slavery on enslaved people.
Avoid simply summarizing the sources. Analyze them! What do they reveal about the system of slavery and its impact on individuals and communities? 🧐
#4. Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the impact of the 1808 ban on the transatlantic slave trade on the institution of slavery in the United States? (A) It led to a decrease in the overall enslaved population. (B) It resulted in the end of domestic slave trade. (C) It increased the reliance on domestic reproduction to expand the enslaved population. (D) It caused a shift in the economy away from cotton production.
-
The term "Second Middle Passage" refers to: (A) The initial voyage of enslaved Africans to the Americas. (B) The forced migration of enslaved people from the upper to the lower South. (C) The journey of enslaved people to freedom via the Underground Railroad. (D) The period of Reconstruction after the Civil War.
-
Abolitionist writers like Frederick Douglass and Frances Ellen Watkins Harper used their writings to: (A) Support the claims of enslavers that slavery was a benevolent institution. (B) Expose the brutality and inhumanity of the slave system. (C) Encourage enslaved people to accept their fate. (D) Argue for the gradual end of slavery through compensation to enslavers.
#Free Response Question
Prompt: Analyze the ways in which the domestic slave trade impacted the lives of enslaved African Americans and contributed to the growth of the cotton industry in the antebellum South. In your response, refer to both the excerpt from Solomon Northup’s Twelve Years a Slave and the Broadside for an Auction of Enslaved Persons at the Charleston Courthouse.
Scoring Breakdown:
- Thesis (1 point): Presents a clear, historically defensible thesis that addresses the prompt.
- Example: The domestic slave trade, fueled by the demand for cotton, led to the forced migration and brutal separation of enslaved families, while simultaneously solidifying the economic power of the Southern planter class.
- Contextualization (1 point): Describes the broader historical context of the domestic slave trade.
- Example: The 1808 ban on the transatlantic slave trade led to an increased reliance on domestic reproduction and the internal slave trade to meet the growing labor demands of the cotton industry.
- Evidence from Sources (2 points): Uses specific evidence from both the Northup excerpt and the broadside to support the argument.
- Example: Northup's account of Eliza's desperate pleas not to be separated from her children illustrates the emotional trauma of family separation, while the broadside demonstrates the commodification of human beings as property to be bought and sold.
- Evidence beyond the sources (2 points): Provides additional evidence beyond the provided sources to support the argument.
- Example: The forced marches of enslaved people in coffles from the upper to the lower South, known as the Second Middle Passage, caused immense physical and psychological trauma, and the expansion of cotton production in the lower South directly led to increased demand for enslaved labor.
- Analysis and Reasoning (2 points): Explains how the evidence supports the argument and demonstrates an understanding of the complexity of the issue.
- Example: The domestic slave trade not only displaced individuals but also shattered families and communities, as loved ones were torn apart and sold to different regions, while the economic benefits of the slave trade further entrenched the institution of slavery and perpetuated racial inequalities.
For FRQs, remember to start with a strong thesis statement, use evidence from the sources, and explain how that evidence supports your argument. Don't forget to include evidence beyond the sources to demonstrate your knowledge! 📝
You've got this! Go get 'em! 💪🏾
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





