Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Ethan Taylor
8 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers the states of matter (solids, liquids, and gases), focusing on their properties such as shape, volume, particle movement, compressibility, flow, and diffusion. Key concepts include density, surface tension, capillary action, and viscosity. It also includes practice questions on these topics and relates them to intermolecular forces (IMFs).
#States of Matter: A Last-Minute Review 🚀
Hey there, future AP Chem master! Let's dive into the states of matter – solids, liquids, and gases – and make sure you're totally prepped for the exam. Remember, this unit is all about understanding how matter behaves, which is crucial for many other topics. Let's get started!
#
Matter and Its States
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It exists in different states, each with unique properties. Understanding these states is fundamental to grasping many other topics in AP Chemistry.
#🧊 Solids
- Structure: Solids can be crystalline (ordered, 3D structure) or amorphous (disordered). Think of salt (crystalline) vs. glass (amorphous).
- Shape & Volume: Solids have a definite shape and volume. They don't expand to fill their container because the particles are tightly packed.
- Particle Movement: Particles vibrate in place but don't move past each other.
- Compressibility: Solids are virtually incompressible.
- Flow: Solids do not flow.
- Diffusion: Diffusion within a solid is extremely slow.
#💧 Liquids
- Shape & Volume: Liquids take the shape of their container but do not expand to fill it. They have a definite volume.
- Particle Movement: Particles can move past each other (fluidity), but they are still close together.
- Compressibility: Liquids are virtually incompressible.
- Flow: Liquids flow readily.
- Diffusion: Diffusion within a liquid occurs slowly.
The solid and liquid phases of a substance have similar molar masses because the particles are closely held together.
#Surface Tension
- Definition: Surface tension is the tendency of liquids to minimize their surface area due to imbalanced intermolecular forces at the surface. 💧


- Trends:
- Stronger IMFs = higher surface tension.
- Higher temperature = lower surface tension.
#Capillary Action
- Definition: Capillary action is the spontaneous rising of a liquid against gravity. Think of a paper towel soaking up spilled water. 🧻
- Forces Involved:
- Cohesive Forces: Forces between liquid molecules.
- Adhesive Forces: Forces between liquid molecules and the container.
- How it Works: Adhesive forces pull surface molecules up, and cohesive forces pull bulk molecules up with them.
- Meniscus:
- Concave Meniscus: (e.g., water in glass) Adhesive forces > cohesive forces. 🧪

- Convex Meniscus: (e.g., mercury in glass) Cohesive forces > adhesive forces.
- Concave Meniscus: (e.g., water in glass) Adhesive forces > cohesive forces. 🧪
#Viscosity
- Definition: Viscosity is a liquid's resistance to flow. Syrup is more viscous than water. 🥞
- Trends:
- Stronger IMFs = higher viscosity.
- Higher temperature = lower viscosity.
#♨️ Gases
- Shape & Volume: Gases assume the shape and volume of their container.
- Particle Movement: Particles move rapidly in straight lines.
- Compressibility: Gases are compressible.
- Flow: Gases flow readily.
- Diffusion: Diffusion within a gas is rapid.

#Density
- Definition: Density (D) is mass per unit volume: D = m/V.
- General Trend: Solids are usually the most dense, and gases are usually the least dense.
#Density Practice Question
A student measured the mass of a sealed 644 mL flask that contained air. The student then flushed the flask with an unknown gas, resealed it, then measured the mass again. The air and the unknown gas were at STP. Calculate the mass of the unknown gas. The density of air at STP is 1.29 g/L.
| Volume of sealed flash | 644 mL |
|---|---|
| Mass of Sealed flask and air | 121.03 g |
| Mass of Sealed Flask and Unknown Gas | 122.60 g |
Solution:
- Mass of Air:
- Convert mL to L: 644 mL = 0.644 L
- Use D = m/V: 1.29 g/L = m / 0.644 L => m = 0.831 g
- Mass of Flask:
- Subtract mass of air from total mass: 121.03 g - 0.831 g = 120.20 g
- Mass of Unknown Gas:
- Subtract mass of flask from total mass with unknown gas: 122.60 g - 120.20 g = 2.40 g
Don't forget to convert units! Always make sure your units match before performing calculations. In this case, converting mL to L was crucial.
#Overview
Think about your everyday experiences to remember the differences between solids, liquids, and gases. Here's a quick visual:
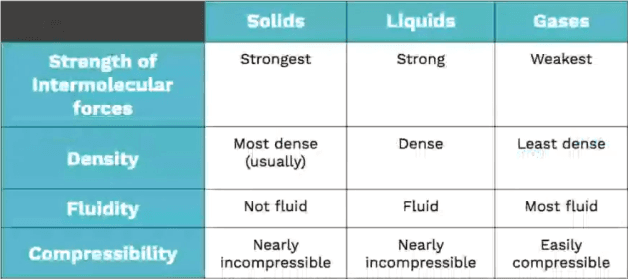
SLiG: Remember the order of states: Solid, Liquid, Gas. It's like sliding down a hill – from most structured to least structured.
#Final Exam Focus
- High-Priority Topics: States of matter, intermolecular forces, density calculations, and the behavior of gases (which we'll cover more in the next section).
- Common Question Types:
- MCQs on properties of different states.
- FRQs involving density calculations or explaining phenomena like surface tension and capillary action.
- Questions combining states of matter with IMFs.
- Last-Minute Tips:
- Review the trends in surface tension, viscosity, and capillary action.
- Practice unit conversions for density problems.
- Focus on understanding the why behind the properties of each state.
#
Practice Question
Practice Questions
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the arrangement of particles in a crystalline solid? (A) Randomly arranged with no long-range order (B) Arranged in a repeating, three-dimensional pattern (C) Closely packed but able to move past each other (D) Widely dispersed and moving rapidly
-
Which property of liquids is most directly related to the strength of intermolecular forces? (A) Compressibility (B) Surface tension (C) Density (D) Vapor pressure
-
A liquid is observed to have a convex meniscus when placed in a glass tube. This observation suggests that: (A) The adhesive forces between the liquid and the glass are stronger than the cohesive forces within the liquid. (B) The cohesive forces within the liquid are stronger than the adhesive forces between the liquid and the glass. (C) The liquid is nonpolar. (D) The liquid is at its boiling point.
#Free Response Question
Consider three different substances: water (H₂O), ethanol (C₂H₅OH), and diethyl ether (C₄H₁₀O). Their properties are summarized below:
| Substance | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Boiling Point (°C) | Density (g/mL) | Surface Tension (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (H₂O) | 18.02 | 100 | 1.00 | 72.8 |
| Ethanol (C₂H₅OH) | 46.07 | 78.3 | 0.789 | 22.3 |
| Diethyl Ether (C₄H₁₀O) | 74.12 | 34.6 | 0.713 | 17.0 |
(a) Explain why water has a significantly higher boiling point than both ethanol and diethyl ether, despite having a much lower molar mass. (b) Based on the data provided, explain the observed trend in surface tension among the three liquids. Be sure to refer to the intermolecular forces present in each substance. (c) If equal volumes of water and diethyl ether are placed in separate graduated cylinders, describe the shape of the meniscus that will be observed in each cylinder. Explain your reasoning.
Scoring Breakdown:
(a) (3 points)
- 1 point for identifying hydrogen bonding in water.
- 1 point for stating that hydrogen bonds are stronger than dipole-dipole forces or London dispersion forces.
- 1 point for explaining that higher boiling points indicate stronger intermolecular forces.
(b) (3 points)
- 1 point for identifying that water has hydrogen bonding, ethanol has hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole forces, and diethyl ether has only London dispersion forces.
- 1 point for stating that stronger IMFs lead to higher surface tension.
- 1 point for correctly relating the strength of IMFs to the observed surface tension trend.
(c) (3 points)
- 1 point for stating that water will have a concave meniscus.
- 1 point for stating that diethyl ether will have a convex meniscus.
- 1 point for correctly relating the meniscus shape to the relative strength of adhesive and cohesive forces.
#Combining Multiple Units
- A gas sample occupies 10.0 L at 27 °C and 1 atm. If the gas is compressed to 5.0 L and the temperature is increased to 127 °C, what is the new pressure of the gas? (Hint: Use the combined gas law and remember to convert temperatures to Kelvin.)
Always double-check your units and make sure they are consistent before you start your calculations. Pay close attention to the question's wording to avoid misinterpreting the given information.
Alright, you've got this! Go crush that exam! 💪
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





