El Niño and La Niña
Jack Wilson
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers El Niño and La Niña, opposite phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). It explains their formation, focusing on trade winds, thermocline shifts, and resulting global climate impacts like altered precipitation and ecological disruptions. It also includes practice questions and exam tips.
#AP Environmental Science: El Niño and La Niña - Your Ultimate Guide
Hey there, future environmental champ! Let's break down El Niño and La Niña, two key players in global climate patterns. This guide is designed to be your go-to resource, especially the night before the exam. Let's get started!
#
Understanding ENSO: El Niño-Southern Oscillation
#
The Basics
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of a natural climate pattern called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Think of it as a giant seesaw of ocean temperatures and atmospheric pressure in the tropical Pacific. These events have a ripple effect on weather and ecosystems worldwide.
#
Memory Aid: ENSO Seesaw
Imagine a seesaw: El Niño is when one side (warm water) goes up, and La Niña is when the other side (cold water) goes up. This helps visualize the opposing nature of these events.
#
El Niño: The Warm Phase
#What is El Niño?
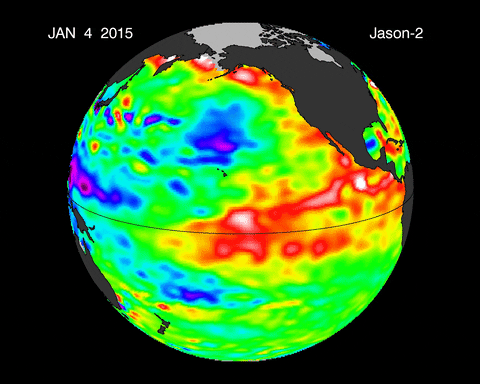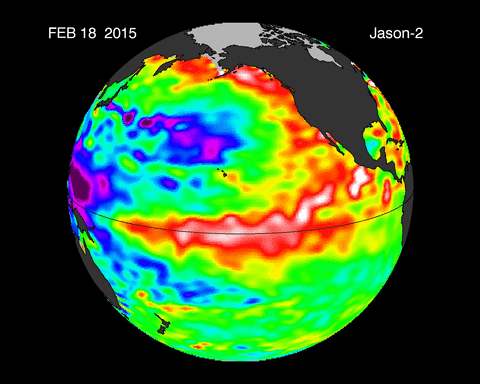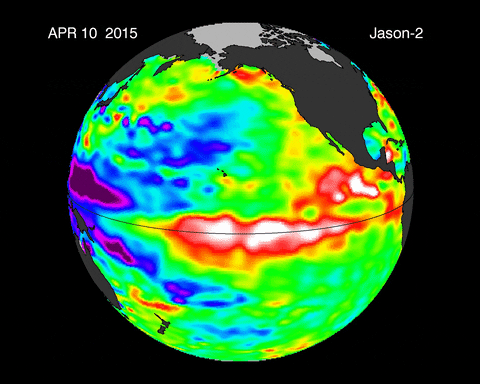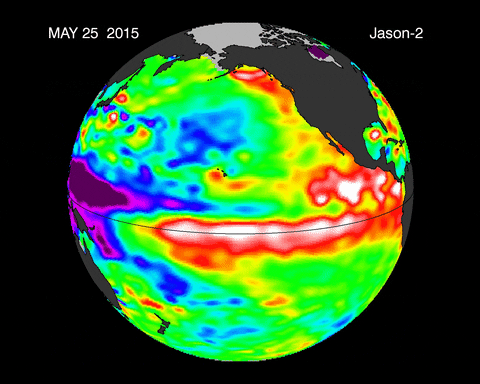
An El Niño event is characterized by a significant warming of the Pacific Ocean surface waters between South America and Papua New Guinea. This warming disrupts normal weather patterns.
#How Does It Happen?
- Weakening Trade Winds: The usual trade winds that blow from east to west across the Pacific weaken or even reverse direction.
- Warm Water Shift: This causes warm surface water to move eastward toward the coast of South America.
- Thermocline Deepens: The thermocline, the layer where a sharp temperature drop occurs, moves deeper into the ocean. This means less cool water is near the surface and more warm water is present. 💡
#El Niño Effects
- Increased Precipitation: Drier regions on the west coast of South America experience higher rainfall, often leading to flooding.
- Colder Winters: The southeastern United States tends to have colder and wetter winters.
- Global Impacts: Changes in ocean temperature can affect weather patterns around the world, potentially leading to droughts in some areas and flooding in others.
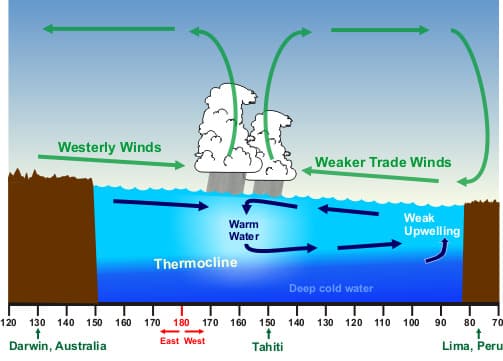
Caption: Illustration of El Niño conditions, showing the eastward shift of warm water and the deepening of the thermocline.
Caption: Animated depiction of the warm water movement during an El Niño event.
#
La Niña: The Cool Phase
#What is La Niña?
La Niña is essentially the opposite of El Niño. It involves a cooling of the Pacific Ocean surface waters in the same region.
#How Does It Happen?
- Strengthened Trade Winds: The trade winds become unusually strong, blowing more intensely from east to west.
- Warm Water Shift: This pushes warm surface water further west, away from the South American coast.
- Upwelling: Colder, deeper water rises to the surface along the coast of South America, a process called upwelling. The thermocline moves upward, reducing the volume of warm water near the surface. 🌊
#La Niña Effects
- Cooler Temperatures: Generally, we see cooler temperatures and wet conditions in many parts of the world.
- Warmer, Drier Conditions: In the southeastern US, La Niña often brings warmer and drier conditions, the opposite of El Niño.
#
Broader Environmental Impacts of ENSO
#Ecological Disruptions
- Species Relocation: Rapid climate changes can force species to relocate if their current habitats become too warm or too cold. This can disrupt ecosystems.
- Migration Changes: Bird migration patterns can be significantly altered, which may affect breeding and survival rates.
#Global Climate Effects
- Ocean Heat Capacity: During El Niño, the ocean's ability to absorb heat decreases, contributing to global warming. 🌡️
- Precipitation Changes: Both El Niño and La Niña cause shifts in precipitation patterns, leading to increased risks of floods and droughts.
#
Exam Tip: Focus on the Opposites
Remember that El Niño and La Niña are opposites. If you understand one, you can often deduce the effects of the other by simply reversing the conditions. Pay attention to how they affect the thermocline, trade winds, and precipitation patterns.
#
Common Mistake: Confusing Local vs. Global Effects
Be careful not to confuse the local effects of ENSO with the global impacts. For example, while El Niño causes wetter conditions in some areas, it can cause droughts in others. Always consider the broader picture.
#
Quick Fact: ENSO Cycle
ENSO events are not regular. They occur every few years, with varying intensity and duration. There is no set schedule for when an El Niño or La Niña will occur, but scientists can predict them.
#Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics
- ENSO Cycle: Understand the basic mechanics of El Niño and La Niña.
- Trade Winds: Know how changes in trade winds drive ENSO events.
- Thermocline: Understand how the thermocline shifts and its implications.
- Global Impacts: Be aware of the broad effects on weather patterns and ecosystems.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Expect questions that test your knowledge of the basic definitions and effects of El Niño and La Niña.
- Free Response: Be prepared to analyze data, explain the mechanisms behind ENSO, and discuss its environmental impacts. Often, FRQs will ask you to connect ENSO to other climate change topics.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back later.
- Read Carefully: Pay close attention to the wording of each question and make sure you understand what is being asked.
- Stay Calm: Take deep breaths, and remember that you are well-prepared. You've got this!
#
Practice Question
Practice Questions
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the conditions during a La Niña event? a) Weakening trade winds and warmer ocean temperatures b) Strengthening trade winds and cooler ocean temperatures c) Deepening thermocline and increased precipitation d) Shallow thermocline and decreased precipitation
-
During an El Niño event, which of the following is most likely to occur? a) Increased upwelling along the coast of South America b) Warmer and drier conditions in the southeastern US c) Shifting of warm water towards the South American coast d) Strengthened trade winds
-
Which of the following is a global impact associated with El Niño? a) Decreased risk of drought in Australia b) Increased ocean heat capacity c) Changes in precipitation patterns leading to floods or droughts d) Cooler temperatures in the southeastern US
#Free Response Question
Question:
El Niño and La Niña are two phases of a climate pattern known as ENSO.
(a) Describe the changes in trade winds and ocean temperatures that occur during both El Niño and La Niña events. (4 points)
(b) Explain how the thermocline is affected during both El Niño and La Niña events. (2 points)
(c) Discuss two potential environmental impacts of El Niño on ecosystems. (2 points)
(d) Explain one way that La Niña can affect weather patterns in the southeastern United States. (1 point)
Scoring Breakdown:
(a) (4 points)
- El Niño Trade Winds: Trade winds weaken or reverse direction. (1 point)
- El Niño Ocean Temperatures: Ocean temperatures increase in the central and eastern Pacific. (1 point)
- La Niña Trade Winds: Trade winds strengthen. (1 point)
- La Niña Ocean Temperatures: Ocean temperatures decrease in the central and eastern Pacific. (1 point)
(b) (2 points)
- El Niño Thermocline: The thermocline deepens. (1 point)
- La Niña Thermocline: The thermocline becomes shallower or moves upward. (1 point)
(c) (2 points)
- Impact 1: Changes in species distribution due to habitat changes (1 point)
- Impact 2: Altered migration patterns of birds (1 point)
(d) (1 point)
- Southeastern US: La Niña can lead to warmer and drier conditions in the southeastern US. (1 point)
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





