Soil Composition and Properties
Liam Thomas
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers soil science fundamentals, focusing on soil composition (sand, silt, clay), soil properties (physical, chemical, and biological), water-holding capacity, the soil texture triangle, and their impact on plant growth. It includes practice questions and tips for the AP Environmental Science exam.
#Soil Science: The Ultimate Study Guide 🌿
Hey there, future AP Environmental Science superstar! Let's dive into the fascinating world of soil, which is way more exciting than it sounds, I promise! This guide is designed to be your go-to resource the night before the exam, so let's make every minute count.
#
Soil Composition and Properties
#Water-Holding Capacity and Retention
- Water-holding capacity is the amount of water soil can hold against gravity.
- Smaller particles = higher water retention. Think of it like tiny sponges!
- Organic matter increases water retention because it acts like a sponge.
- Loam is the goldilocks of soil types, with a balanced mix of particle sizes for optimal water retention.
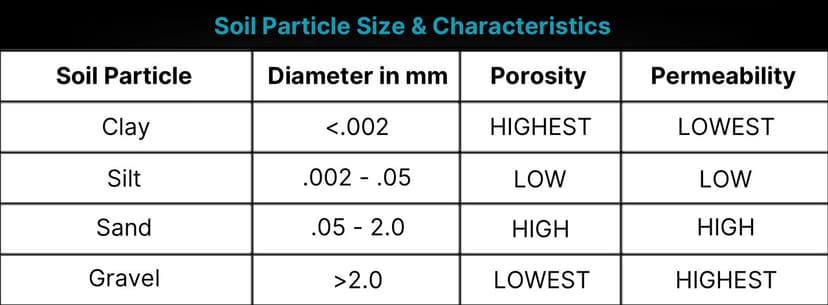
#Particle Sizes and Properties
Remember that soil properties are interconnected. Changes in one area often affect others.
- Porosity: How much pore space there is in soil. Larger particles = larger pores = higher porosity.
- Permeability: How easily water and nutrients move through soil. Larger particles = higher permeability.
- Fertility: The soil's ability to support plant growth. Depends on nutrients (N, P, K), and organic matter.

#Chemical, Physical, and Biological Properties of Soil
#Chemical Properties
Think pH and Cation Exchange when you think about chemical properties.
Don't confuse soil pH with water pH. They are related but not the same. Soil pH is influenced by many factors.
#Physical Properties
Aeration, compaction, permeability, and particle size are all physical properties of soil.
#Biological Properties
Soil is a living ecosystem! Fungi and bacteria play a huge role in soil composition and nutrient cycles.
#Soil Texture Triangle
Practice reading the soil texture triangle. It's a common exam question!

- Used to identify soil type based on the percentage of clay, silt, and sand.
- Follow the lines for each particle type to find the intersection point.
- Example: 20% clay, 50% sand, 30% silt = loam.
Remember the direction of the lines: Clay lines are horizontal, Silt lines go down diagonally, and Sand lines go up diagonally.
#Final Exam Focus 🎯
- High-Priority Topics: Soil composition (sand, silt, clay), water-holding capacity, soil texture triangle, soil properties (physical, chemical, biological).
- Common Question Types:
- Multiple choice questions testing your understanding of soil properties and their relationships.
- Free-response questions (FRQs) asking you to analyze soil data, explain soil processes, or evaluate the impact of human activities on soil.
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back later.
- Common Pitfalls:
- Confusing porosity and permeability.
- Misreading the soil texture triangle.
- Not linking soil properties to plant growth and ecosystem health.
- Strategies:
- Read questions carefully and underline key terms.
- Use diagrams and charts to help you visualize concepts.
- Answer all parts of the FRQs to maximize your score.
#
Practice Question
Practice Questions
#Multiple Choice Questions
- Which soil type has the highest water-holding capacity? (a) Sand (b) Silt (c) Clay (d) Loam
- Which of the following best describes soil permeability? (a) The amount of pore space in soil (b) The ability of water to move through soil (c) The nutrient content of soil (d) The pH of soil
- A soil sample is found to be 60% sand, 20% silt, and 20% clay. According to the soil texture triangle, what type of soil is it? (a) Sandy loam (b) Loamy sand (c) Sandy clay loam (d) Loam
#Free Response Question
A group of students is conducting an experiment to determine the water-holding capacity of different soil samples. They collect three samples: Sample A (mostly sand), Sample B (mostly clay), and Sample C (loam). They pour 100 mL of water into each sample and measure the amount of water that drains out after 30 minutes.
(a) Identify the soil sample that would likely have the highest water-holding capacity. Explain your reasoning. (2 points) (b) Describe how the particle size of each soil sample affects its porosity and permeability. (3 points) (c) Explain how the water-holding capacity of the soil can affect plant growth. (2 points) (d) Describe one human activity that could negatively impact soil water-holding capacity, and explain how it has that impact. (2 points)
#Scoring Breakdown for FRQ:
(a) (2 points) - 1 point for identifying Sample B (mostly clay) as having the highest water-holding capacity. - 1 point for explaining that clay has small particles and thus more surface area, which results in higher water retention.
(b) (3 points) - 1 point for stating that Sample A (sand) has large particles, resulting in high porosity (large pore spaces) and high permeability. - 1 point for stating that Sample B (clay) has small particles, resulting in low porosity (small pore spaces) and low permeability. - 1 point for stating that Sample C (loam) has a mix of particle sizes, resulting in moderate porosity and permeability.
(c) (2 points) - 1 point for explaining that soil with high water-holding capacity can retain water longer, making it available for plant roots. - 1 point for explaining that soil with low water-holding capacity may lead to water stress for plants, as water drains away quickly.
(d) (2 points) - 1 point for describing a valid human activity, such as deforestation, excessive tilling, or soil compaction due to heavy machinery. - 1 point for explaining how the activity reduces water-holding capacity, for example, deforestation reduces organic matter and thus reduces water retention, excessive tilling breaks up soil structure and reduces water retention, and soil compaction reduces the pore space available for water.
Remember, you've got this! Go get that 5! 🚀
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





