Business Cycles
Isabella Lopez
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers the business cycle in macroeconomics, including key economic measures (GDP, unemployment, inflation), and the four phases of the cycle (expansion, peak, contraction, trough). It explains how these measures change throughout the cycle, provides real-world examples and graphs, and offers exam tips, common mistakes to avoid, practice questions, and a mnemonic device.
#AP Macroeconomics: The Business Cycle - Your Night-Before Guide 🚀
Hey! Let's make sure you're totally ready for the exam tomorrow. We're going to break down the business cycle, link it to everything we've learned, and get you feeling confident. Let's dive in!
#
Unit 2: Measuring Economic Health
#
Key Economic Measures
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): The total value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders. Think of it as the economy's overall output. 📈
- Unemployment: The percentage of the labor force that is actively seeking work but cannot find it. It's a crucial indicator of how well the economy is using its resources. 🧑💼
- Inflation: The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and, subsequently, purchasing power is falling. It's important to track to ensure a stable economy. 💰
#The Business Cycle: A Quick Overview
- The economy doesn't grow at a constant rate; it fluctuates. These fluctuations create a cyclical pattern known as the Business Cycle. It's like a rollercoaster with ups (expansions) and downs (contractions).
- Think of it like a heartbeat – it has periods of high activity (expansion) and low activity (contraction). 💓
#
Parts of the Business Cycle
#Visualizing the Cycle
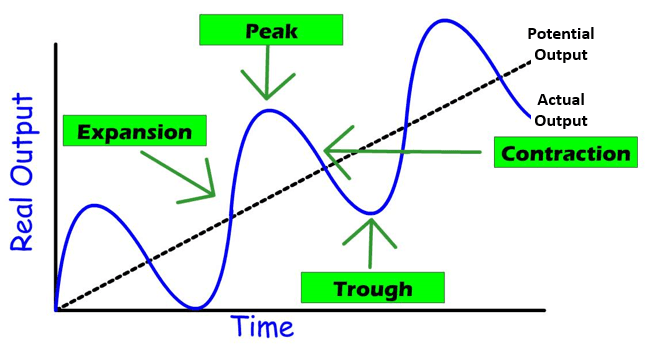
- This graph shows how real GDP (a measure of output) changes over time. The growth trend line represents the ideal, sustainable growth rate.
#1. Expansion Phase (Inflationary Gap)
- What it is: The economy is growing, like a plant sprouting in spring. 🌱
- Key Characteristics:
- GDP is increasing.
- Unemployment is low (more people have jobs). 🧑🏭
- Inflation is rising (prices are going up). ⬆️
- Often referred to as an inflationary gap because actual output exceeds potential output.
#2. Peak
- What it is: The highest point of economic growth, like the top of a mountain. ⛰️
- Key Characteristics:
- Economy is at its maximum output.
- Often, this is followed by a slowdown.
#3. Contraction Phase (Recession/Depression)
- What it is: The economy is shrinking, like a plant wilting in the fall. 🍂
- Key Characteristics:
- GDP is decreasing.
- Unemployment is high (more people are out of work). 🧑 unemployed
- Inflation is low (prices may even fall). ⬇️
- Recession: Two consecutive quarters (6 months) of negative GDP growth. 📉
- Depression: A severe and prolonged recession. Think of the Great Depression as the extreme example. 😟
#4. Trough
- What it is: The lowest point of economic activity, like the bottom of a valley. 🏞️
- Key Characteristics:
- Economy is at its lowest output.
- This is where the cycle starts to turn back up.
#Real-World Examples
#US Real GDP Growth

- Grey areas represent recessions. Notice how GDP growth fluctuates.
#US Unemployment Rate

- Unemployment rises during recessions and falls during expansions. It's like a seesaw with the GDP growth.
Mnemonic for Business Cycle:
- Every Person Can Thrive
- Expansion
- Peak
- Contraction
- Trough
#
Exam Tips
- Connect the Dots: Understand how changes in GDP, unemployment, and inflation are interconnected within the business cycle.
- Graph Analysis: Be comfortable interpreting graphs of GDP and unemployment over time.
- Definitions: Know the definitions of recession and depression.
#
Common Mistakes
- Confusing Expansion and Contraction: Make sure you know which phase is associated with rising GDP and which with falling GDP.
- Misinterpreting Graphs: Pay close attention to the axes and what they represent.
- Forgetting the Definitions: Don't mix up recession and depression.
#Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics:
- Understanding the Business Cycle: Be ready to explain each phase and its characteristics.
- Key Economic Indicators: Know how GDP, unemployment, and inflation relate to the cycle.
- Real-World Application: Be able to analyze real-world data and identify different phases of the cycle.
#Common Question Types:
- Multiple Choice: Questions that test your understanding of definitions and relationships.
- Short Answer: Questions that ask you to explain the different phases of the business cycle.
- Free Response: Questions that require you to analyze graphs and apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios.
#Last-Minute Tips:
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. Move on and come back if you have time.
- Read Carefully: Make sure you understand what the question is asking before you answer.
- Stay Calm: You've got this! Take a deep breath and trust your preparation.
#
Practice Question
Practice Questions
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which phase of the business cycle is characterized by increasing unemployment and decreasing inflation? (A) Expansion (B) Peak (C) Contraction (D) Trough
-
A period of two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth is known as: (A) Depression (B) Expansion (C) Recession (D) Trough
-
During the expansionary phase of the business cycle, which of the following is most likely to occur? (A) Decreasing inflation and increasing unemployment (B) Increasing inflation and decreasing unemployment (C) Decreasing inflation and decreasing unemployment (D) Increasing inflation and increasing unemployment
#Free Response Question
Scenario: The following graph shows the real GDP of a country over a period of time. Assume that the growth trend line represents the natural rate of real GDP growth over time.

(a) Identify the phases of the business cycle labeled A, B, and C on the graph. [3 points]
(b) Describe the typical conditions of unemployment and inflation during phase B. [2 points]
(c) Explain one fiscal policy action the government might take during phase C to stimulate the economy, and explain how this policy action would affect aggregate demand. [3 points]
Scoring Breakdown:
(a)
- 1 point for correctly identifying phase A as Expansion.
- 1 point for correctly identifying phase B as Peak.
- 1 point for correctly identifying phase C as Contraction.
(b)
- 1 point for stating that unemployment is typically low during the peak.
- 1 point for stating that inflation is typically high during the peak.
(c)
- 1 point for identifying a valid fiscal policy action, such as increasing government spending or cutting taxes.
- 1 point for explaining that this action would increase aggregate demand.
- 1 point for explaining how the policy would increase aggregate demand (e.g., increased government spending directly increases AD, tax cuts increase disposable income, which increases consumption and AD).
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





