Production, Cost, and the Perfect Competition Model
Nancy Hill
13 min read
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers production, costs, and perfect competition. It examines factors of production, production measures (TP, MP, AP), and returns to scale. Short-run and long-run costs are explored, including fixed costs (FC), variable costs (VC), total cost (TC), average and marginal costs (ATC, AVC, AFC, MC), and the relationship between cost curves. The guide also discusses types of profit (accounting, economic, normal), profit maximization (MR=MC), and short-run/long-run firm decisions. Finally, it details the characteristics and market equilibrium of perfect competition.
#AP Microeconomics: Unit 3 Study Guide - Production, Costs, and Perfect Competition
Hey there, future AP Micro master! 🎉 Unit 3 is the heart of microeconomics, and it's where everything starts to click. This guide is designed to help you nail down the core concepts, especially the night before the exam. Let's get started!
#Unit 3: The Producer's World
Unit 3 is foundational for Units 4 & 5. Master it here, and you'll be set for the rest of the course!
#Key Questions for Unit 3:
- How do firms decide what to produce and how much?
- What are the different types of costs, and how do they affect production decisions?
- How do firms maximize their profits?
- What does a perfectly competitive market look like, and how does it function?
#3.1: The Production Function
#Factors of Production
- Land: Natural resources.
- Labor: Human effort.
- Capital: Tools, machinery, and equipment.
#Production Measures
- Total Product (TP): Total output produced by a firm.
- Marginal Product (MP): Additional output from one more unit of input (e.g., labor).
- Average Product (AP): Total product divided by the quantity of input (TP/Q).
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns: As you add more of one input (while holding others constant), the marginal product will eventually decrease. 💡
#Returns to Scale
- Increasing Returns: Output increases by a larger proportion than the increase in inputs.
- Constant Returns: Output increases by the same proportion as the increase in inputs.
- Decreasing Returns: Output increases by a smaller proportion than the increase in inputs.
Practice Question
If a firm doubles all of its inputs and output more than doubles, the firm is experiencing: A) Decreasing returns to scale B) Constant returns to scale C) Increasing returns to scale D) Diminishing marginal returns Answer: C
The marginal product of labor is: A) The total output divided by the number of workers B) The additional output from hiring one more worker C) The average output per worker D) The total output produced by all workers Answer: B
A company produces widgets using labor and capital. Initially, with 2 workers and 2 machines, they produce 20 widgets. When they increase labor to 3 workers (while keeping capital at 2 machines), their output increases to 27 widgets. When they add a fourth worker (still with 2 machines), their output increases to 32 widgets. (a) Calculate the marginal product of the third worker. (b) Calculate the marginal product of the fourth worker. (c) Explain whether this firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns and explain why.
(a) 7 widgets (27-20 = 7) - 1 point (b) 5 widgets (32-27=5) - 1 point (c) Yes, the firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns because the marginal product of the third worker (7) is greater than the marginal product of the fourth worker (5). - 2 points
#3.2: Short-Run Production Costs
#Short-Run vs. Long-Run
- Short-Run: At least one input is fixed (e.g., factory size).
- Long-Run: All inputs are variable.
#Types of Costs
- Fixed Costs (FC): Costs that do not vary with output (e.g., rent).
- Variable Costs (VC): Costs that change with output (e.g., wages, materials).
- Total Cost (TC): Sum of fixed and variable costs:
TC = FC + VC
#Per-Unit Costs
- Average Total Cost (ATC): Total cost divided by quantity:
ATC = TC / Q - Average Fixed Cost (AFC): Fixed cost divided by quantity:
AFC = FC / Q - Average Variable Cost (AVC): Variable cost divided by quantity:
AVC = VC / Q - Marginal Cost (MC): Additional cost of producing one more unit.
MC is like the Moving Cost – it shows how much cost changes with each additional unit. Think of it as the 'extra' cost. 🚀
#Cost Curves
- MC intersects ATC and AVC at their minimum points.
- AFC always decreases as quantity increases.
- ATC and AVC are U-shaped due to diminishing returns.

Remember the relationships between the curves: MC pulls ATC and AVC up when it's above them and pulls them down when it's below. 📈
Practice Question
Which of the following is true about the relationship between marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC)? A) MC always intersects ATC at its minimum point. B) When MC is above ATC, ATC is decreasing. C) When MC is below ATC, ATC is increasing. D) MC and ATC are always equal. Answer: A
If a firm's total fixed cost is 200 when producing 10 units, what is the average total cost? A) 20 C) 100 Answer: C
A firm has the following cost structure: Fixed Costs (FC) are 20 when producing 1 unit, 75 for 3 units, and
(a) TC for 1 unit:70, 2 units: 125, 4 units: 70, 2 units: 41.67, 4 units: 25, 3rd unit: 35 - 2 points
#3.3: Long-Run Production Costs
#Long-Run Average Total Cost (LRATC)
- Represents the lowest possible average cost for each output level when all inputs are variable.
- Envelopes all the short-run ATC curves.
#Economies of Scale
- LRATC decreases as output increases. 📉
- Often due to specialization and bulk purchasing.
#Diseconomies of Scale
- LRATC increases as output increases. 📈
- Often due to management challenges and coordination issues.
#Constant Returns to Scale
- LRATC remains constant as output increases.
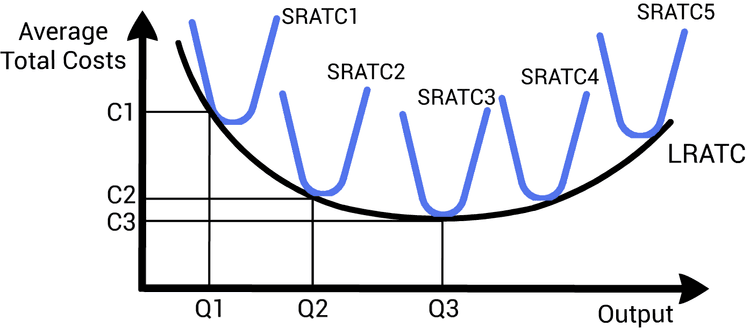
Don't confuse short-run and long-run costs. In the long run, firms can adjust all inputs. 🕰️
Practice Question
Economies of scale are present when: A) Long-run average total cost increases as output increases. B) Long-run average total cost decreases as output increases. C) Long-run average total cost remains constant as output increases. D) Short-run average total cost decreases as output increases. Answer: B
Which of the following is a characteristic of the long run? A) At least one input is fixed. B) All inputs are variable. C) Only labor is variable. D) Only capital is fixed. Answer: B
A firm's long-run average total cost (LRATC) curve shows that as output increases from 100 to 500 units, the LRATC decreases. However, when output increases from 500 to 1000 units, the LRATC increases. (a) Explain what is happening when output increases from 100 to 500 units. (b) Explain what is happening when output increases from 500 to 1000 units. (c) At what output level is the firm operating at the minimum efficient scale?
(a) The firm is experiencing economies of scale, where increasing output leads to lower average costs. - 1 point (b) The firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale, where increasing output leads to higher average costs. - 1 point (c) The firm is operating at the minimum efficient scale at 500 units, where the LRATC is at its lowest point. - 2 points
#3.4: Types of Profit
#Profit Basics
- Profit (π): Total revenue minus total cost:
π = TR - TC - Total Revenue (TR): Price times quantity:
TR = P * Q
#Accounting Profit
- Total revenue minus explicit (monetary) costs.
- What accountants typically measure.
#Economic Profit
- Total revenue minus explicit and implicit (opportunity) costs.
- What economists typically measure.
Think of economic profit as the 'real' profit. It considers what you could have earned elsewhere. 🧐
#Profit Conditions
- Positive Profit:
TR > TC - Losses:
TR < TC - Normal Profit:
TR = TC(Economic profit is zero).
#Marginal Revenue (MR)
- Additional revenue from selling one more unit.
In perfect competition, MR is equal to the market price (P). 💰
Practice Question
Economic profit is calculated as: A) Total revenue minus explicit costs. B) Total revenue minus implicit costs. C) Total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs. D) Total revenue minus accounting costs. Answer: C
A firm is earning a normal profit when: A) Total revenue is greater than total cost. B) Total revenue is less than total cost. C) Total revenue is equal to total cost. D) Accounting profit is zero. Answer: C
A small business owner invests 60,000 salary she could have earned elsewhere. Her business generates 80,000 in explicit costs. (a) Calculate the accounting profit. (b) Calculate the economic profit. (c) Explain the difference between accounting and economic profit in this scenario.
(a) Accounting profit = 80,000 (explicit costs) = 200,000 (revenue) - 60,000 (implicit costs) =
</practice_question>
#3.5: Profit Maximization
#The Profit Maximizing Rule
- Produce where Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC).
- This is the optimal output level for maximum profit. 🎯
<exam_tip> Remember: MR = MC is the golden rule for profit maximization. It applies to all market structures! 🏆 </exam_tip>

<practice_question>
A firm maximizes profit by producing at the output level where: A) Total revenue equals total cost. B) Marginal revenue equals average total cost. C) Marginal revenue equals marginal cost. D) Average revenue equals average cost. Answer: C
If a firm's marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, the firm should: A) Decrease production. B) Increase production. C) Maintain current production levels. D) Shut down production. Answer: B
A firm's marginal cost (MC) and marginal revenue (MR) are given in the table below:
| Output | MC | MR |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | |
| 2 | 15 | |
| 3 | 20 | |
| 4 | 25 | |
| (a) What is the profit-maximizing level of output for this firm? | ||
| (b) Explain why the firm should not produce at an output level of 2. (c) Explain why the firm should not produce at an output level of 4. (a) The profit-maximizing level of output is 3, where MR = MC =20 - 1 point | ||
| (b) The firm should increase production at an output level of 2 because MR (15), indicating that the firm is not maximizing its profit - 1 point | ||
| (c) The firm should not produce at an output level of 4 because MC (20), indicating that the firm would lose money on the fourth unit - 2 points |
#3.6: Short-Run and Long-Run Decisions
#Short-Run Shutdown Rule
- A firm should shut down if Price (P) < Average Variable Cost (AVC) at the profit-maximizing output (MR=MC).
- In the short run, fixed costs are sunk, so only variable costs matter. 🛑
#Long-Run Entry and Exit
- Entry: Firms enter a market when there are positive economic profits.
- Exit: Firms exit a market when there are losses (negative economic profits).
- In the long run, firms will only produce if they make at least a normal profit (zero economic profit). 🚪
Think of the shutdown rule as 'covering your costs'. If you can't cover your variable costs, it's time to shut down! 🚫
Practice Question
A firm should shut down production in the short run if: A) Price is greater than average total cost. B) Price is less than average variable cost. C) Price is less than average total cost. D) Marginal cost is less than marginal revenue. Answer: B
In the long run, firms will exit a market when: A) They are earning positive economic profits. B) They are earning zero economic profits. C) They are incurring losses. D) They are maximizing profit. Answer: C
A firm in a perfectly competitive market has a marginal cost (MC) of 12, and an average total cost (ATC) of 11. (a) Should the firm produce in the short run? Explain why or why not. (b) What will happen to this firm in the long run? Explain why. (c) What will happen to the market in the long run? Explain why.
(a) No, the firm should not produce in the short run because the market price (12), indicating that the firm cannot cover its variable costs. - 1 point (b) The firm will exit the market in the long run because it is incurring losses (negative economic profits). - 1 point (c) In the long run, firms will exit the market, decreasing market supply, and thus increasing the market price. - 2 points
#3.7: Perfect Competition
#Characteristics of Perfect Competition
- Many buyers and sellers.
- Homogeneous (identical) products.
- Free entry and exit.
- Price takers (firms have no market power). ⚖️
#Perfectly Competitive Firm
- Faces a perfectly elastic (horizontal) demand curve at the market price.
- MR = P = Demand
#Market Equilibrium
- In the long run, firms earn zero economic profit (normal profit).
- Price equals the minimum of ATC.

Perfect competition is a benchmark market structure. It's a theoretical ideal, not often seen in the real world. 🌟
Practice Question
Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market? A) Differentiated products. B) High barriers to entry. C) A few dominant firms. D) Price takers. Answer: D
In the long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive market, firms earn: A) Positive economic profit. B) Negative economic profit. C) Zero economic profit. D) Maximum economic profit. Answer: C
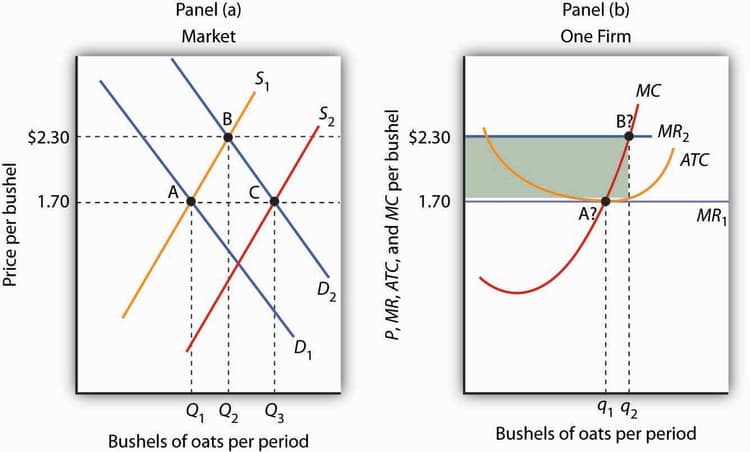
Draw side-by-side graphs for a perfectly competitive market and a representative firm in long-run equilibrium. Label the market price, the firm's demand curve, marginal cost curve, average total cost curve, and the profit-maximizing quantity for the firm. (a) Explain why the firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic. (b) Explain why the firm earns zero economic profit in the long run.
(a) The firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic because it is a price taker and can sell any quantity at the market price. If the firm tries to charge a higher price, it will lose all its customers to other firms selling the same product. - 2 points (b) The firm earns zero economic profit in the long run because if firms are earning positive economic profits, new firms will enter the market, increasing supply and driving down the price until economic profits are zero. If firms are incurring losses, firms will exit the market, decreasing supply and driving up the price until economic profits are zero. - 2 points
#Final Exam Focus
#High Priority Topics
- Cost Curves: Know the relationships between MC, ATC, AVC, and AFC. 📊
- Profit Maximization: Understand MR = MC and its implications. 🎯
- Perfect Competition: Know the characteristics and long-run equilibrium. ⚖️
- Short-Run Shutdown Rule: Understand when to shut down production. 🛑
- Economic vs. Accounting Profit: Know the difference and how to calculate them. 🧐
#Common Question Types
- Graphing: Be able to draw and interpret cost curves and market diagrams. 📈
- Calculations: Practice calculating costs, profits, and marginal values. 🧮
- Scenario Analysis: Apply concepts to real-world situations and make decisions. 🤔
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too much time on one question. Move on and come back if needed. ⏱️
- Read Carefully: Pay close attention to the wording of each question. 🧐
- Show Your Work: For FRQs, clearly show your steps and reasoning. ✍️
- Stay Calm: You've got this! Take deep breaths and trust your preparation. 🧘
Good luck on your exam! You're going to do great! 💪
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





