Firms' Short-Run Decisions to Produce and Long-Run Decisions to Enter or Exit a Market
Paul Scott
9 min read
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers perfectly competitive markets, focusing on firm entry and exit. Key concepts include the shutdown rule (P < AVC), short-run vs. long-run decision-making, impacts of profit and loss on market supply, and achieving long-run equilibrium (zero economic profit). It also provides practice questions with graph analysis and scenario application.
#AP Microeconomics: Market Entry & Exit - Your Night-Before Guide
Hey! Let's get you prepped for the exam with a super focused review of market entry and exit. We'll break down the key concepts, look at some graphs, and make sure you're feeling confident. Let's do this! 💪
#
Perfectly Competitive Markets: The Basics
- Many Sellers: Lots of firms are competing.
- Low Barriers to Entry/Exit: Easy for firms to start or stop production.
- Price Takers: Firms accept the market price; they don't set it.
# Entering vs. Exiting
- Entering: A firm starts producing and selling goods (quantity > 0).
- Exiting: A firm stops producing, but might still exist as a company (quantity = 0).
#
The Shut-Down Rule: Short-Run Decisions
# When to Shut Down
- In the short run, firms have fixed costs they must pay regardless of production.
- Firms compare Total Revenue (TR) to Total Variable Cost (TVC) or Price (P) to Average Variable Cost (AVC).
Shutdown Rule: If P < AVC, the firm should shut down and only pay fixed costs.
- Think: "If you can't cover your variable costs, don't produce! Just pay the fixed costs."
#Visualizing the Shutdown Point
- Below, the firm should shut down because the price (7) at the profit-maximizing quantity (10).

- Caption: The firm will shut down at a quantity of 10 because the price (7).
#Example
- TR = 5/unit)
- TC = 12/unit)
- Loss if operating = 50 -
- Fixed Cost (FC)=50 (AFC of
- Decision: Shut down because50 (fixed cost) < $70 (loss if operating).
- Producer Surplus (PS) = TR - TVC. If P < AVC, PS is negative, which is another way to see why firms shut down.
#
Long-Run Entry and Exit
# Long-Run Decisions
- In the long run, all costs are variable, and firms can fully avoid costs by exiting the market.
- Losses: Firms exit the industry, decreasing supply.
- Profits: Firms enter the industry, increasing supply.
- Firms follow the profit: "If there's profit, they come; if there's loss, they leave."
#Losses Lead to Exit
- Below, the firm is making a loss, so firms will leave the industry in the long run.

- Caption: The firm is making a loss because the price is less than the ATC. Firms will leave the industry in the long run.
#Profits Lead to Entry
- Below, the firm is making a profit, so firms will enter the industry in the long run.

- Caption: The firm is making a profit because the price is greater than the ATC. Firms will enter the industry in the long run.
#Market Impact of Entry and Exit
# Market Adjustments
- Price Takers: Individual firms don't set prices; the market does.
- Entry: Supply shifts right, price decreases (P↓).
- Exit: Supply shifts left, price increases (P↑).
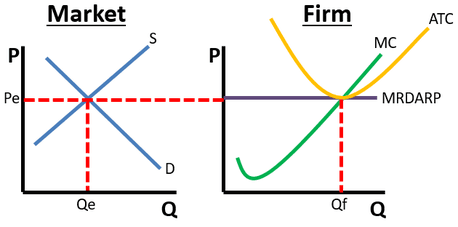
- Caption: The market graph on the left shows how market supply and demand determine price, while the firm graph on the right shows how a firm responds to that price.
- Remember: Market changes drive firm changes. Supply and demand shifts impact the market price, which then affects the individual firm's decisions.
#Long-Run Equilibrium
- In the long run, profits tend toward normal (zero economic profit).
- Profits: Entry drives prices down until profits are zero.
- Losses: Exit drives prices up until losses are zero.
- Think of it like a seesaw: Profits bring more firms, which lowers prices; losses push firms out, which raises prices. Eventually, things balance out at zero economic profit.
#Final Exam Focus
#
Key Topics
- Shutdown Rule: Know when a firm should stop production in the short run (P < AVC).
- Long-Run Entry/Exit: Understand how profits and losses drive firms in and out of the market.
- Market Impact: Be able to explain how entry and exit affect market supply and price.
#
Common Question Types
- Graph Analysis: Be ready to interpret graphs showing cost curves, market supply/demand, and the effects of entry/exit.
- Scenario-Based Questions: Apply the shutdown rule and entry/exit principles to real-world scenarios.
- Long-Run Equilibrium: Explain how competitive markets reach zero economic profit in the long run.
#
Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back later.
- Common Pitfalls: Be careful with short-run vs. long-run distinctions. Remember, fixed costs matter in the short run but not the long run.
- FRQs: Clearly label your graphs and explain your reasoning step-by-step.
#Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
A perfectly competitive firm is producing at a level where its marginal cost is greater than its average variable cost, and its average total cost is greater than the market price. Which of the following must be true? (A) The firm is making an economic profit. (B) The firm is making an economic loss, but should continue to produce in the short run. (C) The firm is making an economic loss and should shut down in the short run. (D) The firm is producing at the allocatively efficient level of output. (E) The firm is producing where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
-
If firms in a perfectly competitive industry are earning positive economic profits, which of the following will most likely occur in the long run? (A) New firms will enter the industry, and the market price will fall. (B) New firms will enter the industry, and the market price will rise. (C) Existing firms will increase their output, and the market price will fall. (D) Existing firms will decrease their output, and the market price will rise. (E) Existing firms will exit the industry, and the market price will rise.
#Free Response Question
Assume that the market for widgets is perfectly competitive. The market is currently in long-run equilibrium.
(a) Draw correctly labeled side-by-side graphs for the widget market and a typical firm in the widget market. On your graphs, show the market price and quantity, the firm’s quantity, and the firm’s average total cost.
(b) Now assume that there is an increase in the demand for widgets. On your graphs in part (a), show the short-run effects of the increase in demand on the market price and quantity, the firm’s quantity, and the firm’s profit or loss. Explain the changes in the market and the firm.
(c) Given your answer to part (b), what will happen to the number of firms in the widget market in the long run? Explain.
(d) On your graphs in part (a), show the long-run effects of the increase in demand on the market price and quantity, the firm’s quantity, and the firm’s profit or loss. Explain the changes in the market and the firm.
#Scoring Guidelines for FRQ:
(a) (3 points) - 1 point: Correctly labeled market graph with downward-sloping demand and upward-sloping supply curves, showing equilibrium price and quantity. - 1 point: Correctly labeled firm graph with a horizontal demand curve at the market price, showing the firm's quantity where P=MC. - 1 point: Correctly showing the firm's ATC curve tangent to the demand curve at the firm's quantity.
(b) (4 points) - 1 point: On the market graph, show a rightward shift of the demand curve, resulting in a higher equilibrium price and quantity. - 1 point: On the firm graph, show the horizontal demand curve shifting up to the new market price and the firm increasing quantity to where P=MC. - 1 point: Correctly show that the firm is earning a profit (P > ATC). - 1 point: Explanation that the increase in demand leads to higher market price and quantity, and the firm increases quantity to maximize profit.
(c) (2 points) - 1 point: Explanation that the positive profit will attract new firms to enter the market. - 1 point: Explanation that the entry of new firms will increase market supply.
(d) (3 points) - 1 point: On the market graph, show the supply curve shifting to the right, resulting in a lower market price and higher market quantity. - 1 point: On the firm graph, show the horizontal demand curve shifting down to the new market price and the firm decreasing quantity to where P=MC. - 1 point: Explanation that the market price decreases until the firm is earning zero economic profit (P=ATC).
That's it! You've got this. Go ace that exam! 🎉
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





