Sine and Cosine Function Values
Henry Lee
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers the unit circle, focusing on its definition, angle measurements (radians and degrees), and trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent). It explains positive and negative angles, multiple revolutions, and using the unit circle to find trigonometric values. The ASTC rule for determining the sign of trigonometric functions in different quadrants is also covered. Finally, the guide provides practice questions and tips for the exam.
#The Unit Circle: Your Ultimate Guide 🧭
Hey there, future AP Pre-Calculus master! Let's dive into the unit circle – your secret weapon for acing the exam. This guide is designed to be your go-to resource, especially the night before the test. No stress, just clear explanations and smart tips to boost your confidence. Let's get started!
#
The Foundation: Understanding the Unit Circle
#What is the Unit Circle?
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1, centered at the origin (0,0) on the coordinate plane. It's the foundation for understanding trigonometry and beyond. Think of it as your visual cheat sheet for trig functions! 💡
- Radius: Always 1 unit.
- Center: Always at the origin (0,0).
- Key Concept: Connects angles to trigonometric values.
#Angles in Standard Position
An angle in standard position starts from the positive x-axis and goes counterclockwise. This is how we measure angles on the unit circle. Remember, counterclockwise is the standard direction. ⏰
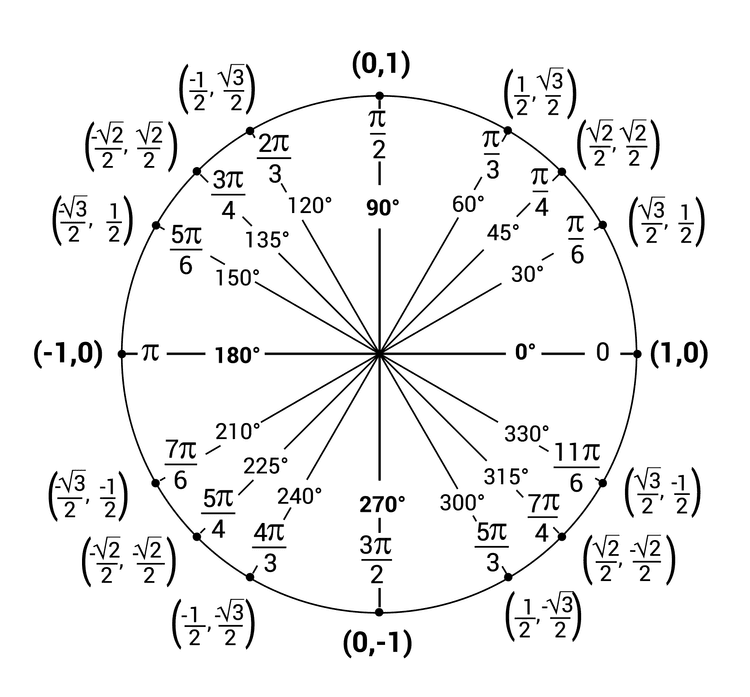
#Navigating the Unit Circle
-
Starting Point: The positive x-axis (0 degrees or 0 radians).
-
Direction: Counterclockwise for positive angles, clockwise for negative angles.
-
Measurements: Angles are shown in both degrees and radians.
#
Angles on the Unit Circle
#Measuring Angles
- Radians and Degrees: The unit circle shows angles in both radians (e.g., π/6) and degrees (e.g., 30°).
- Full Rotation: 360 degrees or 2π radians.
- Reflex Angles: Angles greater than 180° but less than 360°. For example, 300 degrees is a reflex angle. 📐
#Positive and Negative Angles
- Counterclockwise: Positive angles.
- Clockwise: Negative angles. For example, 5π/3 radians (counterclockwise) is the same as -π/3 radians (clockwise).
#Multiple Revolutions
-
Each full revolution adds 2π radians (or 360 degrees) to the angle. If you make 3.5 rotations, you've covered 7π radians.
#
Trigonometry with the Unit Circle
#Point P and Trigonometric Functions
-
Terminal Ray: A line from the origin at a given angle.
-
Point P: The intersection of the terminal ray and the unit circle.
-
Coordinates of P: (cosθ, sinθ), where θ is the angle.
#Sine, Cosine, and Tangent
- Sine (sin θ): The y-coordinate of Point P.
- Cosine (cos θ): The x-coordinate of Point P.
- Tangent (tan θ): sin(θ) / cos(θ) or y/x.
#Example
-
For 30 degrees (or π/6 radians), Point P is (, 0.5).
-
sin(30°) = 0.5
-
cos(30°) =
-
tan(30°) = 0.5 / () =

#
SOHCAHTOA
- SOH: Sine = Opposite / Hypotenuse
- CAH: Cosine = Adjacent / Hypotenuse
- TOA: Tangent = Opposite / Adjacent
#Constant Ratios
-
The trigonometric ratios are constant for a given angle, regardless of the size of the triangle. These are the unit circle's ratios.
#Finding Angles from Trig Values
#Using Cosine
- Given cos(θ) = 1/2: Find where the x-coordinate is 1/2 on the unit circle. This occurs at θ = π/3 (or 60 degrees).
#Using Sine
- Given sin(θ) = -: Find where the y-coordinate is - on the unit circle. This occurs at θ = 4π/3. ## Determining the Sign of Trig Values
#The ASTC Rule
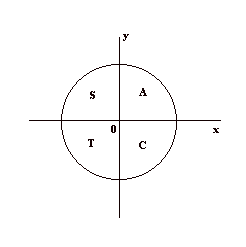
-
Mnemonic: "All Students Take Calculus" (ASTC) helps remember which trig functions are positive in each quadrant. ±
-
Quadrant I (All): All trig functions are positive.
-
Quadrant II (Sine): Only sine is positive.
-
Quadrant III (Tangent): Only tangent is positive.
-
Quadrant IV (Cosine): Only cosine is positive.
#
Final Exam Focus
#High-Priority Topics
- Unit Circle Basics: Understanding angles, radians, and degrees.
- Trigonometric Functions: Sine, cosine, and tangent values.
- ASTC Rule: Determining the sign of trig functions in different quadrants.
- Finding Angles: Given sine or cosine values.
#Common Question Types
- Multiple Choice: Identifying trig values for given angles, or vice versa.
- Free Response: Applying unit circle concepts to solve problems involving triangles, waves, or other periodic functions.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't spend too long on a single question. Move on and come back if needed.
- Common Pitfalls: Double-check your calculations and make sure you're using the correct quadrant.
- Strategies: Use the unit circle as a visual aid. Draw diagrams to help you visualize the problem.
#
Practice Question
Practice Questions
#Multiple Choice Questions
-
What is the value of sin(7π/6)? (A) 1/2 (B) -1/2 (C) √3/2 (D) -√3/2
-
If cos(θ) = -√2/2 and θ is in the second quadrant, what is the value of θ? (A) π/4 (B) 3π/4 (C) 5π/4 (D) 7π/4
-
What is the value of tan(5π/3)? (A) √3 (B) -√3 (C) √3/3 (D) -√3/3
#Free Response Question
Consider a point P on the unit circle corresponding to an angle θ. Given that sin(θ) = -1/2 and cos(θ) > 0:
(a) Determine the exact value of θ in radians for 0 ≤ θ < 2π. (2 points)
(b) Find the exact value of tan(θ). (2 points)
(c) If the radius of the circle were doubled, what would be the new coordinates of point P in terms of the original angle θ? (2 points)
Scoring Breakdown:
(a)
- 1 point: Correctly identifying the quadrants where sin(θ) is negative (III and IV).
- 1 point: Correctly identifying θ = 11π/6 or 330 degrees.
(b)
-
1 point: Correctly finding the value of cos(θ) = √3/2. * 1 point: Correctly calculating tan(θ) = sin(θ)/cos(θ) = (-1/2) / (√3/2) = -√3/3. (c)
-
1 point: Understanding that doubling the radius will double the x and y coordinates.
-
1 point: Correctly stating the new coordinates as (2cos(θ), 2sin(θ)) or (√3, -1).
Good luck, you've got this! 💪
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





