Solutions and Mixtures
Ethan Taylor
7 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers solutions in chemistry, including homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures. It explains key concepts like solutes, solvents, solvation, hydration, and molarity. It also discusses solution formation energy, dilution using the M1V1=M2V2 equation, and provides practice questions and exam tips.
#Solutions: Your Ultimate AP Chem Study Guide 🧪
Hey there, future AP Chem rockstar! Let's dive into the world of solutions, making sure you're totally prepped for anything the exam throws your way. We'll break down everything from mixtures to molarity, keeping it chill and easy to understand.
#Mixtures: Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
First things first, let's quickly recap mixtures. Remember, in AP Chem, we're usually talking about heterogeneous mixtures where the composition isn't uniform, like soil 🪴. You can see the different parts, and the properties change depending on where you look.
Homogeneous mixtures, on the other hand, are uniform throughout. Think salt water 🌊 – you can't see the individual salt and water components.
Here's a visual to help you remember:

#Image Courtesy of Wikipedia
#What Exactly Are Solutions?
Solutions are a type of homogeneous mixture where one substance (the solute) is evenly dispersed within another (the solvent). The solute gets totally surrounded by the solvent – it's like a cozy hug at the molecular level! 🤗
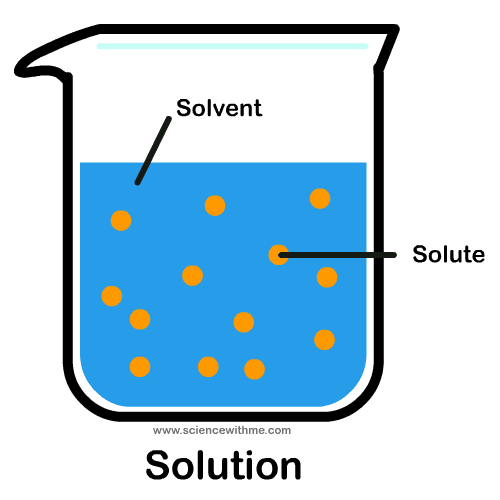
#Image Courtesy of Pinterest
#Examples of Solutions
Solutions can be solids, liquids, or gases:
- Solid Solutions (Alloys):
- Steel (carbon in iron) 🍳
- Brass (zinc in copper) 🎺
- Liquid Solutions:
- Salt water (salt in water) 🧂
- Sugar water (sugar in water) 🍬
- Lemonade (sugar and lemon juice in water) 🍋
- Gas Solutions:
- Air (nitrogen, oxygen, etc.) 💨
- Carbonated water (CO2 in water) 🥤
Think of solutions as a 'uniform mix' where one substance (solute) is dispersed evenly in another (solvent).
#Interactions in Solutions
Solvation is the process where solvent molecules surround solute particles. When the solvent is water, it's called hydration. Basically, the solute gets a water molecule bodyguard! 🛡️
#Representing Solution Composition: Molarity
Concentration is how much solute is in a solution. The most important measure for AP Chem is molarity (M).
Molarity (M) = moles of solute / liters of solution
Molarity is moles of solute per liter of solution, not solvent!
For example, a solution with 24 moles of HCl in 2 liters of water has a molarity of 12 M.
#Other Ways to Represent Concentration
While mass percent and molality aren't on the AP exam, it's good to know them for future studies!
#Forming a Solution: Energy Considerations
Forming a solution involves a few steps, each with its own energy requirements:
- Expand the solute: Separating solute particles
- Expand the solvent: Making space for solute
- Solute-solvent interactions: Forming new attractions

#Image Courtesy of Fiveable's Unit 3 Review
#Diluting Solutions
Dilution is when you decrease the concentration of a solution by adding more solvent.
Remember, dilution doesn't change the number of moles of solute, just the concentration!
We use the equation: M1V1 = M2V2
- M1 and V1 are the molarity and volume of the original solution.
- M2 and V2 are the molarity and volume of the diluted solution.
#How Does Dilution Work?
M1V1 = M2V2 works because (Molarity * Volume) = moles, and the moles of solute stay constant during dilution. You're just spreading the same number of solute particles in a larger volume. Think of it like adding more water to your juice - it becomes less concentrated, but the amount of juice (solute) stays the same. 🧃
M1V1 = M2V2 is your best friend for dilution problems. Just plug and chug!
#Final Exam Focus
- Molarity calculations are a must-know!
- Understand the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
- Be able to explain solvation and hydration.
- Master the M1V1 = M2V2 equation for dilutions.
- Remember that moles of solute remain constant during dilution.
#Last-Minute Tips
- Time Management: Don't get bogged down on one question. Move on and come back if you have time.
- Common Pitfalls: Watch out for unit conversions (mL to L, g to kg).
- FRQ Strategy: Show your work! Even if you don't get the right answer, you can earn points for correct setup.
#Practice Questions
Practice Question
#Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.0 g of NaOH (molar mass = 40.0 g/mol) in enough water to make 500.0 mL of solution? (A) 0.25 M (B) 0.50 M (C) 1.00 M (D) 2.00 M
- Which of the following is NOT a homogeneous mixture? (A) Air (B) Saltwater (C) Vegetable Soup (D) Brass
- A 200 mL solution of 0.5 M NaCl is diluted to 500 mL. What is the final concentration of the solution? (A) 0.1 M (B) 0.2 M (C) 0.5 M (D) 1.25 M
#Free Response Question
A student is asked to prepare 250.0 mL of a 0.200 M solution of copper(II) sulfate (, molar mass 159.6 g/mol).
(a) Calculate the mass, in grams, of needed to make 250.0 mL of a 0.200 M solution. (b) The student uses a volumetric flask to prepare the solution, but accidentally adds 275.0 mL of water instead of 250.0 mL. Calculate the actual concentration of the solution. (c) The student then decides to dilute 50.0 mL of the solution from (b) to a final concentration of 0.0500 M. Calculate the final volume of the diluted solution. (d) Describe the steps the student should take to prepare the solution in (c) using a volumetric flask and any other necessary glassware.
#Scoring Breakdown
(a) Calculation of mass of (3 points)
- 1 point for calculating moles of :
- 1 point for using the molar mass of :
- 1 point for correct answer with units: 7.98 g
(b) Calculation of actual concentration (2 points)
- 1 point for recognizing the moles of remain constant: 0.0500 mol
- 1 point for calculating the new concentration:
(c) Calculation of final volume (2 points)
- 1 point for correctly using
- 1 point for correct answer with units:
(d) Description of steps (3 points)
- 1 point for measuring the correct volume of the stock solution using a graduated cylinder or pipette.
- 1 point for adding the stock solution to a volumetric flask.
- 1 point for adding water to the volumetric flask until the solution reaches the calibration mark and mixing the solution well.
You've got this! Go ace that exam! 🚀
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





