Cold War & Decolonization
Ethan Taylor
8 min read
Listen to this study note
#AP World History: Modern - Unit 8 Study Guide: The Cold War & Decolonization 🌍
Hey! Let's get you prepped for Unit 8. We're diving into the post-WWII world, focusing on the Cold War and Decolonization. Think of this as your ultimate cheat sheet for acing the exam! 🚀
#
Context: The Aftermath of WWII
World War II was a HUGE turning point. It didn't just end a war; it reshaped global power dynamics. Think of it as a reset button for the world, leading directly to the Cold War and the push for decolonization.
#The Seeds of Conflict: Pre-WWII Tensions
- WWI's Unresolved Issues: Nationalism, militarism, imperialism, and alliances were the main ingredients for WWI. The Treaty of Versailles failed to address these issues, setting the stage for further conflict.
- Rise of Fascism: Economic struggles in Germany led to the rise of Hitler and the Nazi Party, who used scapegoating (Jews and Slavs) to gain power.
- WWII Kick-Off: Hitler's invasion of Poland in 1939 started WWII. The Axis (Germany, Italy, Japan) fought against the Allies (USA, France, Britain, USSR, among others).
#
Post-War Power Shift
- Two Superpowers Emerge: The USA and USSR came out of WWII as the dominant world powers. Unlike other allies, they were relatively unscathed by the war.
- Clash of Ideologies: The USA was capitalist, while the USSR was communist, leading to a power struggle.
- The Cold War Begins: This power vacuum after WWII is the main reason for the Cold War. It was a period of tension, espionage, and proxy wars, not direct fighting between the USA and USSR.
- Decolonization: WWII weakened colonial powers, leading to independence movements in Africa and Asia.

#
Big Ideas: Cold War & Decolonization
# The Cold War: Capitalism vs. Communism ⚔️
- Power Struggle: The USA and USSR competed for global dominance, representing capitalism and communism, respectively.
- NATO vs. Warsaw Pact: Countries aligned themselves into military alliances: NATO (USA and allies) and the Warsaw Pact (USSR and allies).
- Divided Germany: Germany was split into East and West, with Berlin also divided. The Berlin Wall became a symbol of Cold War tensions.
- Proxy Wars: Instead of direct conflict, the USA and USSR fought in proxy wars like the Korean and Vietnam Wars. These were symbolic battles between capitalism and communism.
- Indirect Hostilities: Espionage, propaganda, and the constant threat of nuclear war defined the Cold War. Mutually assured destruction (MAD) prevented direct nuclear conflict.
- Ideological Tensions: The space race was a key example of the ideological and technological competition between the two superpowers.
# Decolonization: Independence Movements ✊
- Weakened Colonial Powers: WWII weakened European colonial powers, creating opportunities for independence movements.
- Negotiated Independence: Some colonies, like India, achieved independence through peaceful means (e.g., boycotts, negotiations).
- Violent Independence: Others, like Vietnam and Algeria, had to fight wars to gain their freedom.
- New Nations: Decolonization led to the creation of new states, such as Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Israel, sometimes resulting in conflict.
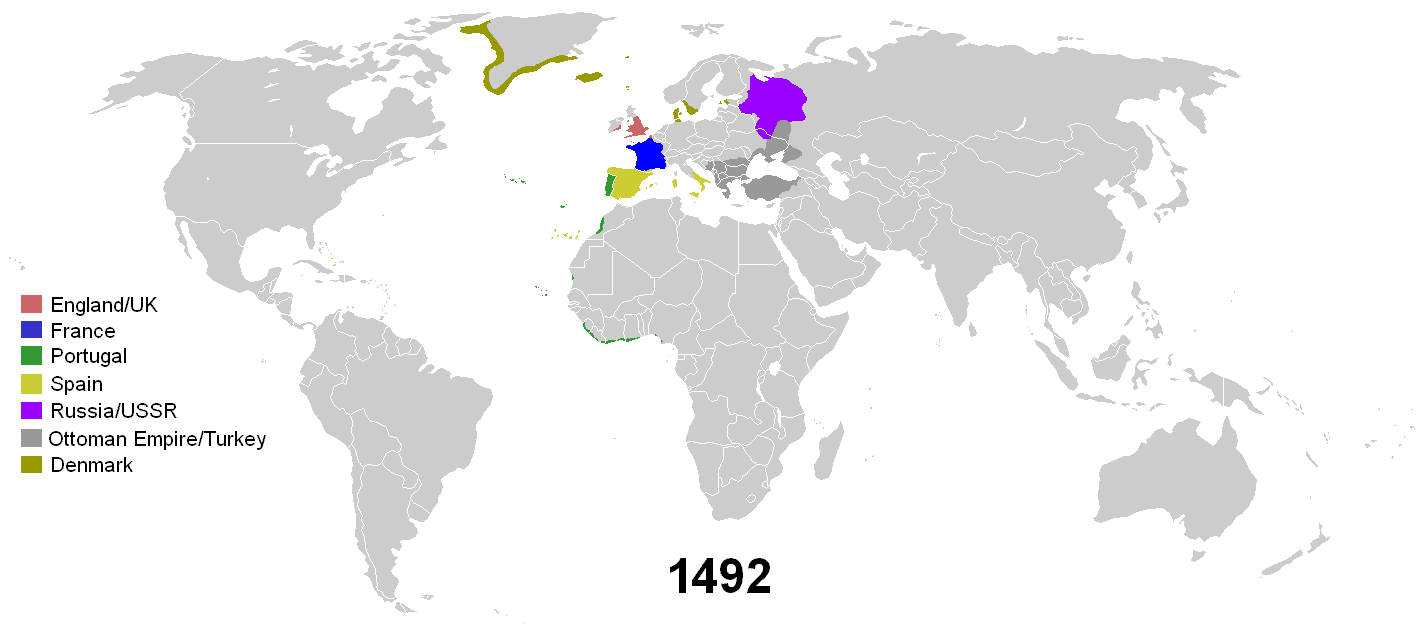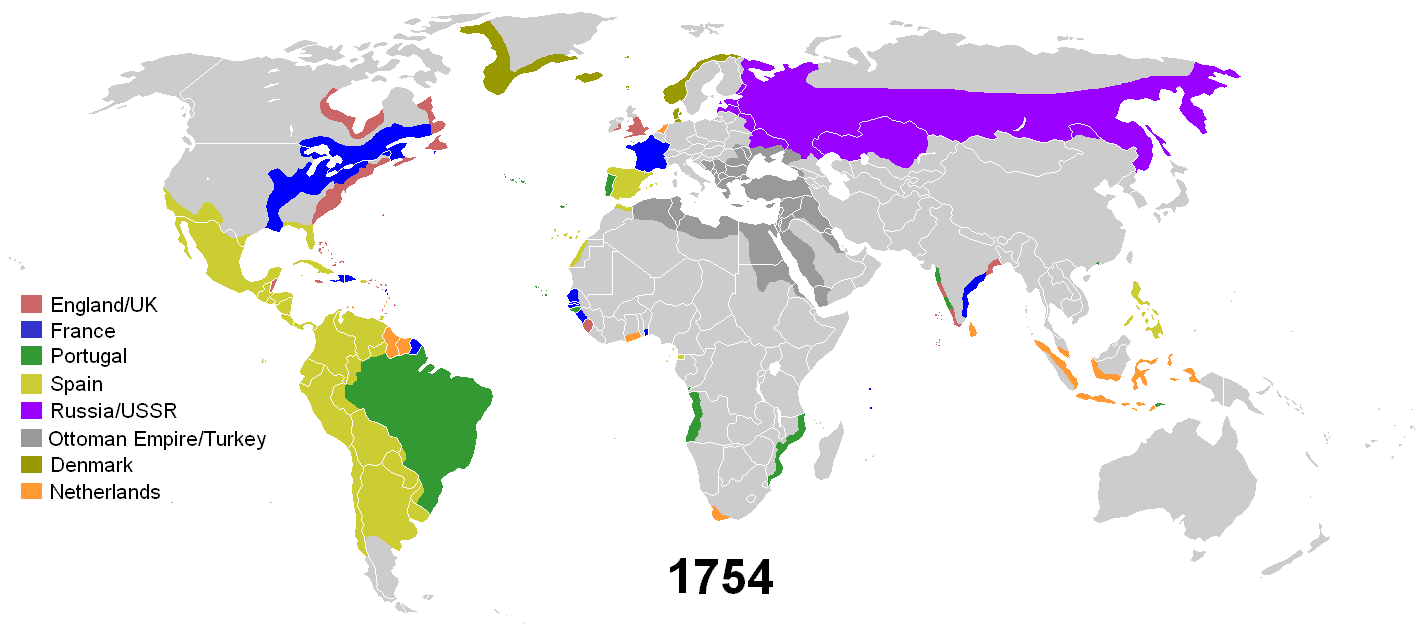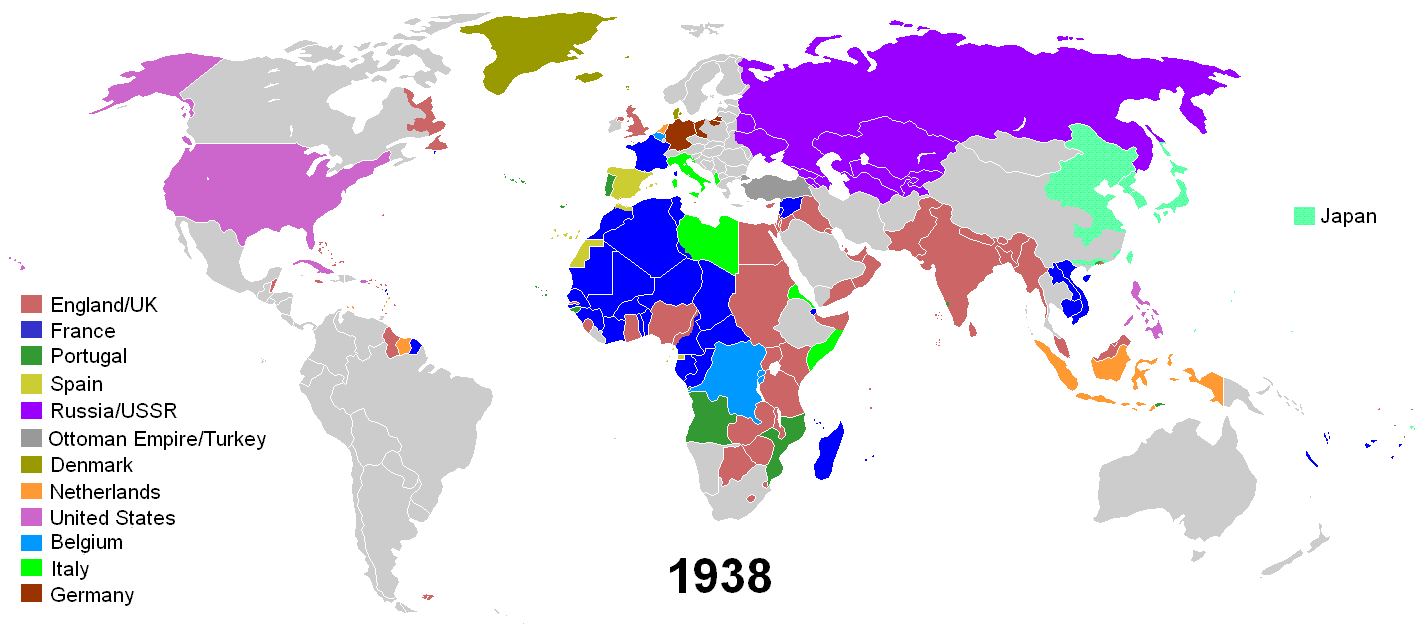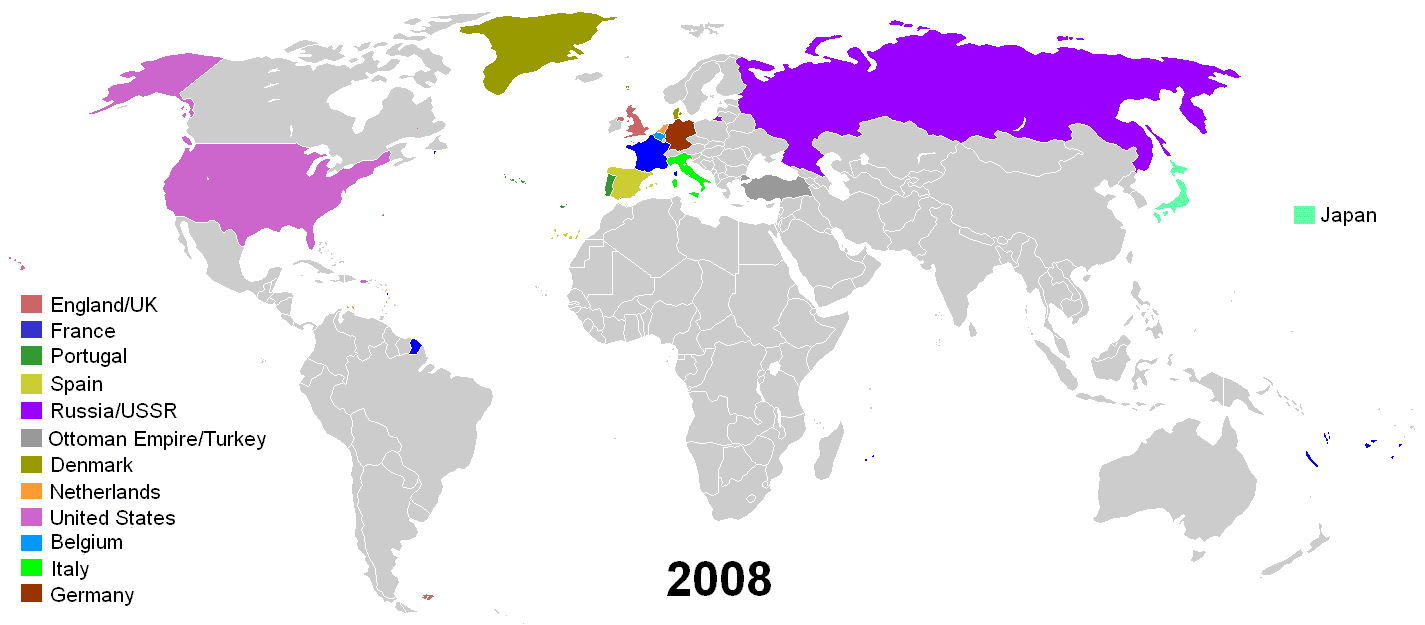 *Image: A GIF showing the decolonization of Africa. Notice how many countries gained independence in the 1960s.*
#
Main Events Timeline
- 1914-1918: World War I
- 1918-1920: Estonian war for independence
- 1919: Gandhi’s first satyagraha; Egyptian Revolution; Syrian National Congress convenes
- 1919: May 4th Movement
- 1929: Great Depression begins
- 1929-1947: Indian protest for independence
- 1931-32: Japanese invasion of Manchuria
- 1933: Great Depression ends
- 1939: World War II starts
- 1945: World War II ends/Yalta and Potsdam conferences
- 1947: Marshall Plan
- 1948: Israel created
- 1949: NATO formed//China established as a communist country
- 1950-53: Korean War
- 1955: Bandung Conference
- 1957: Ghanaian independence
- 1959-1975: Vietnam War
- 1960: Year of Africa (independence of 17 African nations, such as Nigeria and Cameroon)
- 1962: Cuban Missile Crisis
- 1963: Kenyan independence
- 1974-1990: Pinochet in Chile
- 1975-2002: Angolan Civil War
- 1989: Year of independence of many countries from the Soviet bloc/collapse of the Berlin Wall
#
Discussion Questions (Think Like an AP Historian!)
- How did the results of WWII lead to the Cold War and decolonization?
- What were the long- and short-term causes of the Cold War?
- What factors led to the different organizations of new states and how?
- How was the Cold War similar in the Western and Eastern Hemispheres? How was it different?
#
Memory Aid: Cold War & Decolonization
- Cold War = "C"onflict of "C"apitalism vs. "C"ommunism: Remember the 3 C's! The Cold War was all about the conflict between these two ideologies.
- Decolonization = "D"ismantling of "D"ominance: Decolonization is the process of dismantling the dominance of colonial powers.
- Post-WWII = Power Vacuum: The end of WWII created a power vacuum that led to the Cold War and decolonization.
#
Final Exam Focus
- Highest Priority Topics: The causes and effects of the Cold War, the different paths to decolonization, and the formation of new nations.
- Common Question Types: Multiple-choice questions focusing on key events and concepts, short answer questions comparing different decolonization movements, and free-response questions analyzing the impact of the Cold War on global politics.
- Time Management: Quickly identify the main point of the question and use your time wisely. Don't get bogged down in details you don't remember.
- Common Pitfalls: Avoid oversimplifying complex events. Remember to consider both long-term and short-term causes and effects.
- Strategies for Challenging Questions: Start with what you know, and then try to make connections to other concepts. Don't be afraid to brainstorm before writing your answer.
#
Helpful Resources
- Practice LEQ #3: Continuity and Change after 1900
- Practice FRQ #1: Totalitarian vs. democratic states and violence
- Practice LEQ #4: Political ideologies challenging traditional order
- Practice LEQ #4: State involvement in the economy
- Quizlet - Cold War: Cold War
- Quizlet - Cold War (deeper): Cold War (a little deeper)
- Quizlet - Communism/Decolonization: Communism/Decolonization
- Quizlet - Cold War/Decolonization: Cold War/Decolonization
- Quizlet - Decolonization: Decolonization
#Review with Friends 👯
After studying on your own, invite some friends to a study session to discuss the main points and review anything that you may be confused on. It's a great way to have some efficient study time!
Practice Question
#Practice Questions
Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes the primary goal of the Marshall Plan? (A) To establish military bases in Western Europe (B) To promote free trade among European nations (C) To rebuild the economies of Western European countries (D) To spread communism throughout Europe
-
The Bandung Conference of 1955 was significant because it: (A) Established the United Nations (B) Formed the Warsaw Pact (C) Promoted non-alignment among newly independent nations (D) Created the European Union
-
Which of the following is an example of a proxy war during the Cold War? (A) The Cuban Missile Crisis (B) The Berlin Blockade (C) The Korean War (D) The Space Race
Free Response Question
Analyze the social and political effects of the Cold War on TWO of the following regions:
- Latin America
- Africa
- Southeast Asia
Scoring Breakdown
- Thesis (1 point): Presents a historically defensible thesis/claim that responds to all parts of the question. The thesis must establish a line of reasoning.
- Contextualization (1 point): Describes a broader historical context relevant to the prompt. This could include events leading up to the Cold War, such as the end of WWII or the rise of communism.
- Evidence (2 points): Provides specific examples of social and political effects of the Cold War in two of the regions. For each region, you need to give at least one specific piece of evidence. For example, for Latin America, you could mention the Cuban Revolution or the US-backed coups. For Africa, you could discuss the Angolan Civil War or the rise of authoritarian regimes. For Southeast Asia, you could discuss the Vietnam War or the domino theory.
- Analysis and Reasoning (2 points): Explains how the evidence supports the argument. This includes explaining the connections between the Cold War and the social and political effects in those regions. For example, you could discuss how the US and USSR supported different sides in proxy wars, or how the Cold War led to ideological divisions within countries. You also need to make a connection between the social and political effects in those regions.
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





