Decolonization After 1900
Caleb Thomas
7 min read
Listen to this study note
#Decolonization: A Night-Before Review 🌍
Hey there, future AP World History master! Let's break down decolonization – a HUGE topic – into bite-sized pieces. You've got this!
#What is Decolonization?
Decolonization is basically the process where colonies gained independence from their colonizers, mostly after World War II. Think of it as the world map going through a major glow-up! 💡 It's not just about political independence; it's also about cultural and economic freedom. This involved a lot of changes and wasn't always smooth sailing.
Decolonization reshaped the global landscape, leading to the emergence of many new nations in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean. It's a key example of how global power dynamics shifted in the 20th century.
#Key Drivers of Decolonization:
- Nationalism: People wanted to rule themselves! They were tired of being controlled by outsiders.
- Anti-Colonial Movements: Organized groups actively fought for independence through protests, strikes, and sometimes armed conflict.
- International Pressure: The global community, including the newly formed United Nations, often supported decolonization.
#Where Did Decolonization Happen?
Let's zoom in on some specific examples. Remember, each region had its own unique story, but the overall theme is the same: people fighting for their freedom!
#India 🇮🇳
-
Key Player: Mahatma Gandhi led the Indian National Congress (INC) with non-violent protests.
-
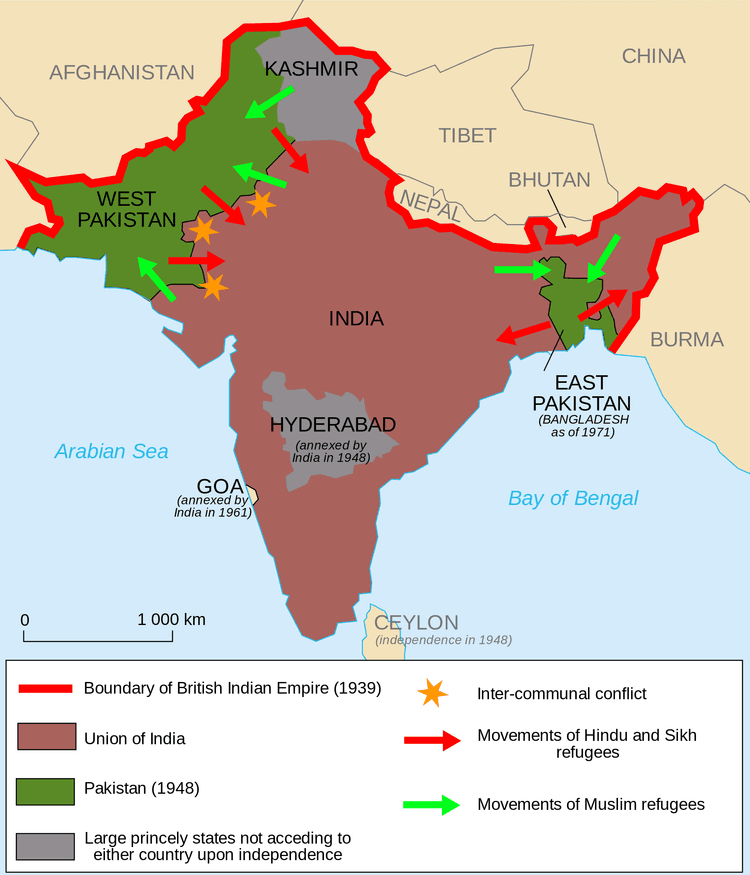
What Happened: India gained independence in 1947 and was then partitioned into India and Pakistan.
#British Gold Coast (Ghana) 🇬🇭
- Key Player: Kwame Nkrumah, a Western-educated nationalist.
- What Happened: Ghana gained independence peacefully in 1957 after boycotts and the formation of the Convention People’s Party.
#Kenya 🇰🇪
- Key Event: The Mau Mau movement, a violent anti-colonial uprising.
- What Happened: Kenya gained independence in 1963 after a period of intense conflict.
The Mau Mau movement was primarily composed of members of the Kikuyu ethnic group, fighting against British colonial rule and land policies.
#Canada 🇨🇦
- Key Event: The Quebecois separatist movement.
- What Happened: Quebecois nationalists sought independence or greater autonomy but were unsuccessful in separating from Canada.
#French Indochina (Vietnam) 🇻🇳
- Key Player: Ho Chi Minh, leader of the Indochinese Communist Party.
- What Happened: Vietnam fought for independence, leading to significant conflict and civilian casualties.
#French West Africa 🇫🇷
- What Happened: This region broke into several independent West African nations after protests and the French passing loi-cadre, which allowed for local governance. By 1960, the region had successfully negotiated independence.
#Algeria 🇩🇿
- Key Event: The National Liberation Front (FLN) waged a guerilla war against the French.
- What Happened: Algeria gained independence in 1962 after a violent struggle, with significant casualties on both sides.
#Nigeria 🇳🇬
- Key Event: The Biafra secessionist movement.
- What Happened: Nigeria gained independence in 1960, but faced a secessionist movement by the Igbo people, which led to a civil war.
#Angola 🇦🇴
- What Happened: Angola declared independence but faced resistance from the Portuguese, leading to a war. The power vacuum created by decolonization led to the Angolan Civil War.
Remember the regions using this: India, Ghana, Kenya, Canada, Vietnam, French West Africa, Algeria, Nigeria, Angola - I Got Kids Very Funny At Night Always
#Review Game - Matching
Let's see if you've got this! Match each term to its correct category.
CATEGORIES:
- Countries that negotiated independence
- Countries that warred for independence
- Secessionist movements
Terms
- Angola
- Biafra
- French West Africa
- Kenya
- Algeria
- Quebecois
- British Gold Coast/Ghana
- India
#Answers
| Negotiated independence | Warred for Independence | Secessionist Movements |
|---|---|---|
| French West Africa, Ghana, India | Angola, Kenya, Algeria | Biafra, Quebecois |
#Final Exam Focus
Okay, time to zoom out and think about the big picture. Here’s what you should focus on for the exam:
Key Themes:
- Nationalism: How it drove decolonization movements.
- Methods of Decolonization: Peaceful vs. violent transitions.
- Post-Colonial Challenges: Economic, political, and social issues faced by newly independent nations.
Time Management: Don't get bogged down in the details of one region. Focus on the overall trends and patterns. Make sure you understand the difference between negotiated and violent independence movements.
#Common Question Types:
- Multiple Choice: Expect questions that test your knowledge of specific events, leaders, and regions. Pay attention to the causes and consequences of decolonization.
- Short Answer Questions (SAQs): Be ready to explain the factors that led to decolonization and compare different independence movements.
- Free Response Questions (FRQs): These will likely ask you to analyze the impact of decolonization on global politics, economics, or culture. Practice comparing different decolonization experiences.
Don't: Get bogged down in the details of one specific region. Focus on broad themes and comparisons. For example, be ready to compare and contrast the decolonization experiences of India and Algeria.
#Last-Minute Tips:
- Stay Calm: You've prepared for this! Take deep breaths and trust your knowledge.
- Read Carefully: Make sure you understand what the question is asking before you start writing.
- Plan Your Essays: Spend a few minutes outlining your arguments before you begin writing your FRQs.
- Don't Leave Anything Blank: Even if you're not sure, write something! You might get partial credit.
For FRQs: Start with a clear thesis statement, use specific historical evidence to support your claims, and analyze the significance of your evidence. Remember, it's not just about knowing the facts; it's about showing you understand them.
#Practice Questions
Okay, let's put your knowledge to the test with some practice questions!
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions
-
Which of the following best describes a major similarity between the decolonization processes in India and Ghana? (A) Both involved violent armed conflicts. (B) Both were led by communist parties. (C) Both were largely peaceful and negotiated. (D) Both resulted in the immediate establishment of democratic governments.
-
The Mau Mau movement in Kenya is best characterized as a: (A) peaceful negotiation for independence (B) violent anti-colonial uprising (C) secessionist movement (D) communist revolution
-
Which of the following was a significant factor contributing to the decolonization of French West Africa? (A) The rise of communist movements (B) The implementation of the loi-cadre (C) The direct intervention of the United Nations (D) The defeat of France in World War II
Short Answer Question (SAQ)
Briefly explain ONE way in which decolonization in Algeria differed from decolonization in Ghana. Briefly explain ONE reason for this difference.
Free Response Question (FRQ)
Analyze the political, economic, and social effects of decolonization in TWO of the following regions:
- India
- Algeria
- French West Africa
Scoring Breakdown for FRQ
- Thesis (1 point): Presents a historically defensible thesis that establishes a line of reasoning.
- Evidence (2 points): Provides specific examples of political, economic, and social effects of decolonization in two chosen regions.
- Analysis and Reasoning (2 points): Analyzes the effects of decolonization by explaining how they impacted the chosen regions. Demonstrates an understanding of the complex processes of decolonization by connecting the evidence to the thesis.
- Complexity (1 point): Demonstrates a nuanced understanding of decolonization by considering multiple perspectives or alternative explanations.
Answer Key:
MCQ: 1. (C), 2. (B), 3. (B)
SAQ: Algeria's decolonization involved a violent war, while Ghana's was largely peaceful. This difference was mainly due to the French's strong resistance to Algerian independence, as they viewed Algeria as an integral part of France, unlike their relationship with Ghana.
FRQ: (Answers will vary, but should include specific examples and analysis of political, economic, and social effects in two of the chosen regions. For example, for India, one might discuss the partition and its social impact, the economic challenges of a newly independent nation, and the establishment of a democratic political system.)
You've got this! Go ace that exam! 💪
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





