Politics and Regional Interests
Daniel Miller
9 min read
Listen to this study note
Study Guide Overview
This study guide covers challenges to national unity in the early 19th century including the Essex Junto, Hartford Convention, and Burr Conspiracy. It examines Native American resistance, focusing on Tecumseh, Tenskwatawa, Tecumseh's War, and the First Seminole War. Henry Clay's American System, including its key components and opposition, is also discussed. Finally, it explores the Panic of 1819 and the Missouri Compromise.
#AP US History Study Guide: Early 19th Century
Hey there, future AP US History champ! Let's dive into the early 1800s. We'll make sure you're not just memorizing, but understanding the big picture. Think of this as your secret weapon for test day! 🚀
#1. Challenges to National Unity
#1.1. Secessionist Movements
- Essex Junto: A group of disgruntled Federalists from New England who felt their influence was waning. They were NOT happy campers! 😠 *
They plotted to secede and form a "Northern Confederacy" with parts of Canada. This shows how fragile the idea of national unity was at this time.
*
The Essex Junto's plan included New York and New Jersey, not just New England.
Remember, the Hartford Convention happened during the War of 1812, which the Federalists opposed.
* They proposed amendments to the Constitution to protect their interests, but it was too late. The war ended, and they looked like whiners. 😩
*
Don't confuse the Hartford Convention with the Constitutional Convention. They are VERY different!
*
Think of the Hartford Convention as the Heartbreak for the Federalists, leading to their demise.
#1.2. The Burr Conspiracy
- Aaron Burr: Former VP, who was a bit of a wild card. He had a plan (or two!) that weren't exactly on the up-and-up. *
Burr killed Alexander Hamilton in a duel before this!
* He traveled to New Orleans and was accused of plotting to create an independent state in the West. 🗺️
*
He was charged with treason, highlighting the fragility of the young nation's stability.
*
Don't confuse Burr's actions with the Essex Junto. They were separate events, but both showed internal divisions.
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions:
-
The Hartford Convention, a meeting of Federalist delegates, was primarily a reaction to: (A) The Louisiana Purchase (B) The Embargo Act of 1807 and the War of 1812 (C) The election of Thomas Jefferson (D) The XYZ Affair
-
Aaron Burr's alleged conspiracy involved: (A) Leading a slave rebellion in Virginia (B) Plotting to secede New England from the Union (C) Establishing a new republic in the West (D) Assassinating President James Madison
Free Response Question:
Analyze the causes and consequences of the Hartford Convention. In your response, be sure to address the following:
- The political climate that led to the convention.
- The specific demands and resolutions proposed by the delegates.
- The impact of the convention on the Federalist Party and the nation as a whole.
Scoring Guide:
- Thesis (1 point): A clear, historically defensible thesis statement that addresses the causes and consequences of the Hartford Convention.
- Context (1 point): Explanation of the political climate of the War of 1812 and Federalist grievances.
- Causes (2 points): Discussion of Federalist opposition to the war, perceived abuses of power, and economic grievances.
- Demands (2 points): Explanation of the proposed constitutional amendments and resolutions.
- Consequences (2 points): Analysis of the convention's impact on the Federalist Party's decline and the perception of disloyalty.
#2. Native American Resistance
#2.1. Westward Expansion and Conflict
- The US was expanding rapidly, often at the expense of Native Americans. 😥 *
Treaties like the Treaty of Fort Wayne often resulted in Native Americans being cheated out of their land.
*
Don't assume all Native American tribes were united. They had their own unique cultures and alliances.
#2.2. The Prophet and Tecumseh
- Tenskwatawa (The Prophet): A Shawnee religious leader who called for a return to traditional ways and rejection of American goods. 🚫 *
Think of the Prophet as the 'anti-tech' guy of his time. He wanted to go back to basics.
- Tecumseh: Tenskwatawa's brother, a brilliant military leader who organized a confederacy to resist American expansion. 💪 *
Tecumseh's Confederacy was a major challenge to US authority in the Old Northwest.
#2.3. Tecumseh's War and the First Seminole War
- Battle of Tippecanoe (1811): William Henry Harrison defeated Tecumseh's forces, making Harrison a national hero. 🏆 *
Remember Harrison's role here; it helps explain his later political success.
- Tecumseh's War (1811-1813): A series of conflicts between the US and Native American tribes in the Old Northwest. *
Tecumseh's death in 1813 effectively ended the confederacy's resistance.
- First Seminole War (1817-1818): Andrew Jackson invaded Spanish Florida, partly to deal with Seminole raids. 🔥 *
The Seminole War was also about runaway slaves who had found refuge with the Seminoles.
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions:
-
The religious leader known as "The Prophet" was primarily known for: (A) Leading a military campaign against the United States (B) Advocating for assimilation with American culture (C) Preaching a message of spiritual revival and resistance to American goods (D) Negotiating treaties with the United States government
-
The Battle of Tippecanoe was significant because it: (A) Resulted in a major victory for Tecumseh's Confederacy (B) Marked the end of the War of 1812 (C) Led to the removal of all Native Americans from the Old Northwest (D) Increased tensions between the United States and Native American tribes
Short Answer Question:
Explain the role of both Tenskwatawa and Tecumseh in the Native American resistance movement during the early 19th century. Be sure to address their individual contributions and the relationship between their efforts.
#3. Economic Nationalism and the American System
#3.1. Henry Clay's Vision
- Henry Clay's American System: A plan to make the US economically self-sufficient. 💰 *
Think of the American System as the 'economic glue' that was supposed to bind the nation together.
*
It aimed to reduce dependence on Europe and promote internal development.
#3.2. Key Components
- Rechartering of the Bank of the US: To stabilize currency and provide credit. *
The Second Bank of the US was chartered in 1816.
- Protective Tariffs: To promote American manufacturing. *
The Tariff of 1816 was a key example of this policy.
- Federal Funding for Internal Improvements: Roads, canals, etc., to improve trade and communication. 🛣️ *
Not all internal improvements were funded at the federal level. States often had to step in.
#3.3. Opposition
- Many argued that the American System was unconstitutional and favored some regions over others. 🙅 *
Opponents argued it was an unfair burden on the states.
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions:
-
The primary goal of Henry Clay's American System was to: (A) Promote states' rights and limited government (B) Establish a free trade agreement with Europe (C) Make the United States economically self-sufficient (D) Expand slavery into new territories
-
A key component of the American System was: (A) The dismantling of the national bank (B) The lowering of tariffs on imported goods (C) Federal funding for internal improvements (D) The abolition of slavery
Short Answer Question:
Explain the three main components of Henry Clay's American System and how they were intended to promote economic growth and national unity. Be sure to discuss the intended benefits of each component.
#4. Economic Downturn and the Missouri Compromise
#4.1. The Panic of 1819
- The Second Bank of the US tried to control inflation, leading to a major economic downturn. 📉 *
Think of the Panic of 1819 as an 'economic hangover' from the rapid expansion of the early 1800s.
*
Land speculation, declining agricultural prices, and bank failures all contributed to the panic.
*
Many state banks closed, and people lost their jobs and homes.
#4.2. The Missouri Compromise (1820)
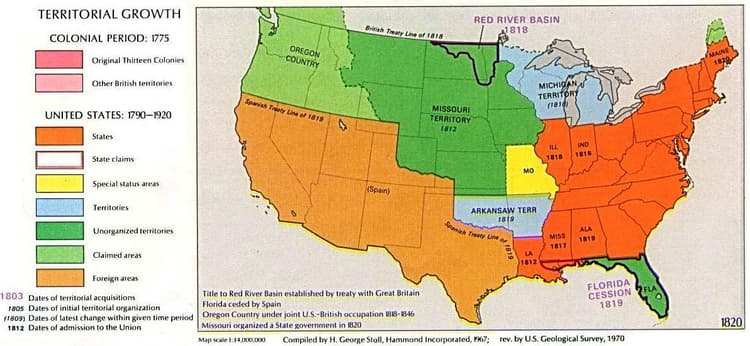
- Missouri's Application for Statehood: Missouri wanted to enter the Union as a slave state, which upset the balance between free and slave states. ⚖️ *
The Tallmadge Amendment was proposed to limit slavery in Missouri, but it failed in the Senate.
- Henry Clay's Solution: Maine was admitted as a free state, and Missouri was admitted as a slave state. Slavery was prohibited in the Louisiana Purchase territory north of the 36°30′ parallel. 🗺️ *
Remember the 36°30′ line; it's crucial for understanding the compromise.
*
The Missouri Compromise was a temporary fix, not a permanent solution.
Practice Question
Multiple Choice Questions:
-
The Panic of 1819 was primarily caused by: (A) A decrease in tariffs on imported goods (B) The failure of the First Bank of the United States (C) Over-speculation in land and bank failures (D) The outbreak of the War of 1812
-
The Missouri Compromise of 1820: (A) Prohibited slavery in all new territories (B) Allowed slavery in all new territories (C) Admitted Maine as a free state and Missouri as a slave state (D) Resolved all issues related to slavery
Free Response Question:
Analyze the causes and consequences of the Missouri Compromise. In your response, be sure to address the following:
- The political and economic context that led to the compromise.
- The specific provisions of the compromise.
- The long-term impact of the compromise on the issue of slavery in the United States.
Scoring Guide:
- Thesis (1 point): A clear, historically defensible thesis statement that addresses the causes and consequences of the Missouri Compromise.
- Context (1 point): Explanation of the balance between free and slave states and the issue of slavery in new territories.
- Causes (2 points): Discussion of Missouri's application for statehood, the Tallmadge Amendment, and the sectional tensions.
- Provisions (2 points): Explanation of the admission of Maine and Missouri, and the 36°30′ line.
- Consequences (2 points): Analysis of the compromise as a temporary solution and its long-term impact on the issue of slavery.
#Final Exam Focus
The Missouri Compromise, the American System, and Native American resistance are often featured in both MCQs and FRQs.
Expect questions that ask you to analyze the causes and effects of events, as well as compare and contrast different viewpoints.
Don't spend too long on any one question. If you're stuck, move on and come back later.
Be sure to connect events to broader themes, not just memorize facts in isolation.
Alright, you've got this! Take a deep breath, review these notes, and go ace that AP exam! You're more prepared than you think. 💪
Continue your learning journey

How are we doing?
Give us your feedback and let us know how we can improve





